Find Scalar Vs Vector Projection Youtube

Find Scalar Vs Vector Projection Youtube My vectors course: kristakingmath vectors courselearn how to find the scalar projections and vector projections of a onto b. the scalar pro. Are you wondering how to find scalar and vector projections? perhaps you have no idea what the component of b onto a is? well have no fear this video will.

Calculus 3 Vector Projections Orthogonal Components Youtube What is a scalar projection and what is the difference between a scalar and a vector projection. i demonstrate how the "shadows" work and how to determine t. The scalar projection is the magnitude of the vector projection. to calculate the scalar projection, square the components of the vector projection, add them and then square root. for example, if the vector projection is 3i 4j, then the scalar projection is √ (32 42) = 5. In this lesson we’ll look at the scalar projection of one vector onto another (also called the component of one vector along another), and then we’ll look at the vector projection of one vector onto another. we’ll follow a very specific set of steps in order to find the scalar and vector projections of one vector onto another. Scalar projection. the scalar projection (or scalar component) of a vector a onto a vector b, also known as the dot product of a and b, represents the magnitude of a that is in the direction of b. essentially, it is the length of the segment of a that lies on the line in the direction of b. it is calculated as |a|cos (θ), where |a| is the.
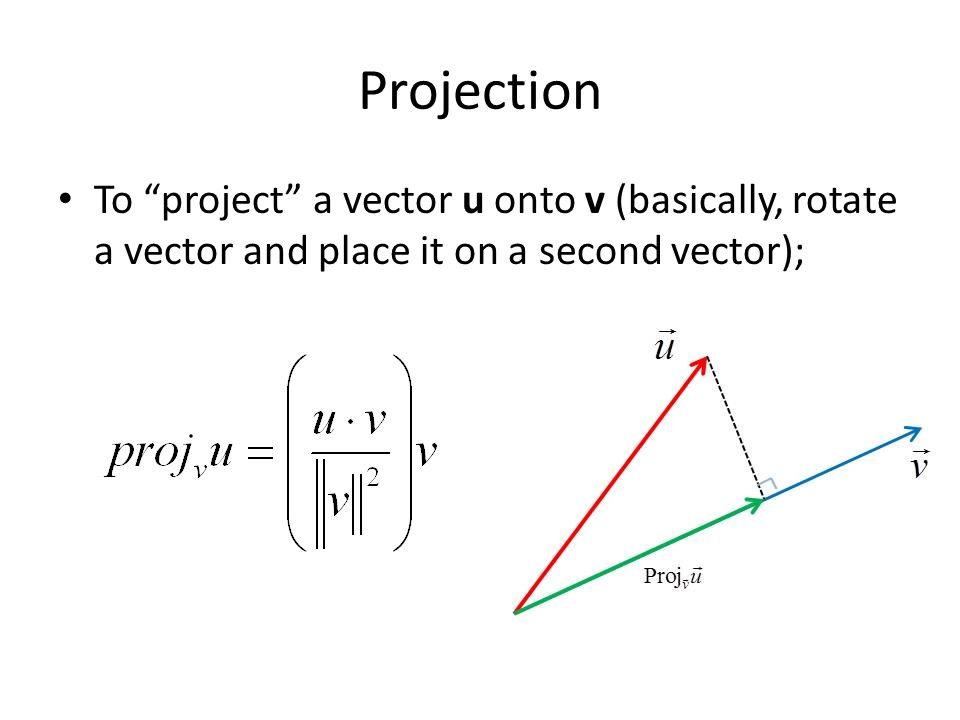
Vector Projection At Vectorified Collection Of Vector Projection In this lesson we’ll look at the scalar projection of one vector onto another (also called the component of one vector along another), and then we’ll look at the vector projection of one vector onto another. we’ll follow a very specific set of steps in order to find the scalar and vector projections of one vector onto another. Scalar projection. the scalar projection (or scalar component) of a vector a onto a vector b, also known as the dot product of a and b, represents the magnitude of a that is in the direction of b. essentially, it is the length of the segment of a that lies on the line in the direction of b. it is calculated as |a|cos (θ), where |a| is the. Example 1. the diagram below shows both vectors ab and d together on the same grid. determine the scalar projection of vector ab onto the direction of vector d solution. to find the scalar projection onto the direction of another vector we need to know the unit vector in the direction of vector d. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Scalars And Vectors Physics Video Scalar Vs Vector Quantities Example 1. the diagram below shows both vectors ab and d together on the same grid. determine the scalar projection of vector ab onto the direction of vector d solution. to find the scalar projection onto the direction of another vector we need to know the unit vector in the direction of vector d. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.

How To Find And Prove The Scalar Component And Vector Projection Of A

Comments are closed.