Everything About Circle Theorems In 3 Minutes

Circle Theorems Notes вђ Corbettmaths This is a graphic, simple and memorable way to remember the difference from a chord or a tangent or a segments and sectors! i made this after struggling to u. Learn everything you need to know about circle theorems in this comprehensive higher gcse maths video tutorial.

Circle Theorems Notes вђ Corbettmaths Solved examples on circle theorems. in the circle given below, triangle abc is inscribed in the circle and the tangent de meets the circle at the point b. find the measure of angle “x” and “y.”. solution: we know that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is equal to 180. ∠bac ∠acb ∠abc = 1800. Finding a circle's center. we can use this idea to find a circle's center: draw a right angle from anywhere on the circle's circumference, then draw the diameter where the two legs hit the circle; do that again but for a different diameter; where the diameters cross is the center! drawing a circle from 2 opposite points. Example 3: consider the circle given below with center o. find the value of y using the circle theorems. solution: to find the value of y, we will use the circle theorem 'the angle subtended by a chord at the center is twice the angle subtended by it at the circumference. '. so, ∠por = 2∠pqr. 3. key circle theorems: a) angles in the same segment: any angle stemming from the same chord or segment within a circle will consistently be equal. it’s a principle rooted in consistent geometry and is one of the key circle theormens to understand. b) the central and inscribed angle relationship: a central angle is always twice the size of.
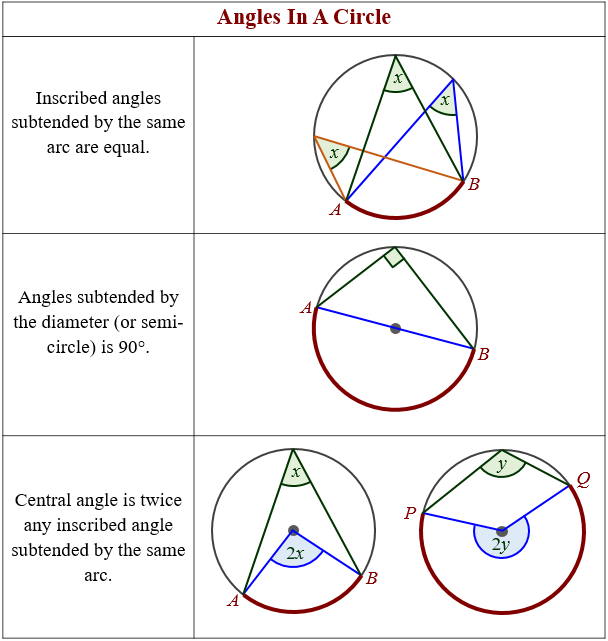
Angles In A Circle Theorems Video Lessons Examples Step By Step Example 3: consider the circle given below with center o. find the value of y using the circle theorems. solution: to find the value of y, we will use the circle theorem 'the angle subtended by a chord at the center is twice the angle subtended by it at the circumference. '. so, ∠por = 2∠pqr. 3. key circle theorems: a) angles in the same segment: any angle stemming from the same chord or segment within a circle will consistently be equal. it’s a principle rooted in consistent geometry and is one of the key circle theormens to understand. b) the central and inscribed angle relationship: a central angle is always twice the size of. This geometry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into circle theorems. it contains plenty of examples and practice problems.circles area, circum. The inscribed angle theorem states that when two chords intersect in a circle, the measure of the inscribed angle formed is equal to one half the measure of its intercepted arc. circle theorems in geometry refer to the various properties and relationships between circles and angles formed by chords, tangents, and secants of a circle.

Comments are closed.