Ecological Footprint Over Time Infographic Population Education

Population And Carbon Emissions Over Time Infographic Population Topics: ecological footprints, interdependence in nature. infographic compares the number of earths needed to provide for humans’ current consumption over time. earth graphics are used to compare the total human population’s ecological footprint in 1970, 1995, and 2022. data is from the global footprint network. Ecological footprint over time infographic earth graphics display human's growing global footprint from 1970 to 1995 to 2022. tool.

Increase Of Climate Related Disasters Infographic Population Education By lauren carlson | january 9, 2015. an ecological footprint is the measure of the human demand on earth’s ecosystems and environment. it’s measured in a way that compares our consumption of natural resources and waste creation with the ability of our planet to regenerate those natural resources and absorb our waste. ecological footprints. Watch your step! introduction. when we hike in the forest, walk on the beach, or play in the snow, we leave behind a mark – our footprint. but the outline of our shoe is not the true size of the impact we make on the earth. less often seen, yet more important, is our ecological footprint. an ecological footprint is a measure of the amount of. The ecological footprint tracks the use of productive surface areas. typically these areas are: cropland, grazing land, fishing grounds, built up land, forest area, and carbon demand on land. on the supply side, a city, state or nation’s biocapacity represents the productivity of its ecological assets (including cropland, grazing land, forest. Fodafo was established in 2019 by york university and global footprint network to be the stewards of those national footprint and biocapacity accounts. the accounts measure the ecological resource use and resource capacity of nations over time. based on approximately 15,000 data points per country per year, the accounts calculate the footprints.
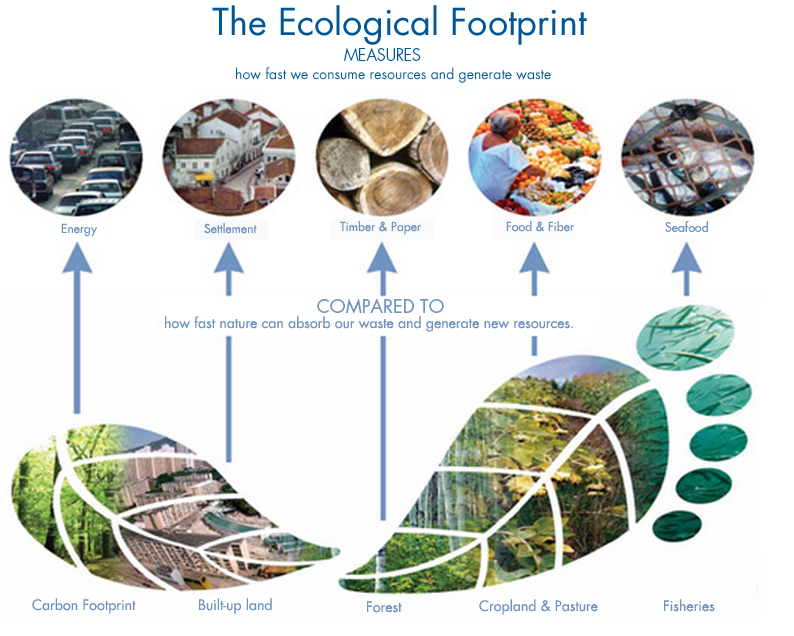
Ecological Footprint Global Footprint Network The ecological footprint tracks the use of productive surface areas. typically these areas are: cropland, grazing land, fishing grounds, built up land, forest area, and carbon demand on land. on the supply side, a city, state or nation’s biocapacity represents the productivity of its ecological assets (including cropland, grazing land, forest. Fodafo was established in 2019 by york university and global footprint network to be the stewards of those national footprint and biocapacity accounts. the accounts measure the ecological resource use and resource capacity of nations over time. based on approximately 15,000 data points per country per year, the accounts calculate the footprints. At the time, it reported that humanity’s ecological footprint exceeded the planet’s biocapacity by about 30% in 1997. the current national footprint and biocapacity accounts (2022 edition), which have been improved over the years, mostly with more robust data sources, still show that global overshoot was 33% for 1997, as opposed to 75% for. “the earth is the lord's and the fullness thereof, the world and those who dwell therein.” psalm 24. 1. introduction. the risk to the future of humanity from the combination of population growth, depletion of resources and destruction of the environment has been forewarned for decades by a series of reports and studies, such as the 1972 report on limits to growth from the club of rome.

Comments are closed.