Dna Definition Function Structure And Discovery Biology Dictionary

Dna Structure And Functions Ninth Grade Biology Dna definition. deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. dna is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. large compressed dna molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, are mostly present inside the. Dna molecules are polymers and are made up of many smaller molecules, called nucleotides. each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar molecule, and a nitrogenous base. dna molecules consist of two dna strands, which are twisted around one another to form a spiral shape known as the double helix. the double helix structure of dna was.

Dna Definition Function Structure And Discovery Biology Dictionary Dna structure and functions. dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, a macromolecule that carries genetic information in all living organisms, from the tiniest microorganisms to the most complex multicellular humans. dna is a fundamental molecule that holds life’s blueprint. within a eukaryotic cell (plant and animal), they are found inside the. Dna, organic chemical of complex molecular structure found in all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. it codes genetic information for the transmission of inherited traits. the structure of dna was described in 1953, leading to further understanding of dna replication and hereditary control of cellular activities. Apart from storing genetic information, dna is involved in: replication process: transferring the genetic information from one cell to its daughters and from one generation to the next and equal distribution of dna during the cell division. mutations: the changes which occur in the dna sequences. transcription. Two major types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). deoxyribonucleic acid (biology genetics definition): a helical double stranded nucleic acid that is crucial for containing the genetic information for cell growth, division, and function. abbreviation: dna. variant: desoxyribonucleic acid.

Dna Definition Function Structure And Discovery Biology Dictionary Apart from storing genetic information, dna is involved in: replication process: transferring the genetic information from one cell to its daughters and from one generation to the next and equal distribution of dna during the cell division. mutations: the changes which occur in the dna sequences. transcription. Two major types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). deoxyribonucleic acid (biology genetics definition): a helical double stranded nucleic acid that is crucial for containing the genetic information for cell growth, division, and function. abbreviation: dna. variant: desoxyribonucleic acid. Dna structure dna is made up of mol ecul es cal l ed nucleot i des. e ach nucleot i de cont ai ns a phosphate group, a sugar group and a ni t rogen base. t he f our t ypes of nitrogen bases are adeni ne (a), t hymine (t ), guani ne (g ) and cyt osine (c). the order of these b ases i s what det ermines dna' s instructions, or genet i c code. Citation: pray, l. (2008) discovery of dna structure and function: watson and crick. nature education 1( 1 ) :100 the landmark ideas of watson and crick relied heavily on the work of other scientists.
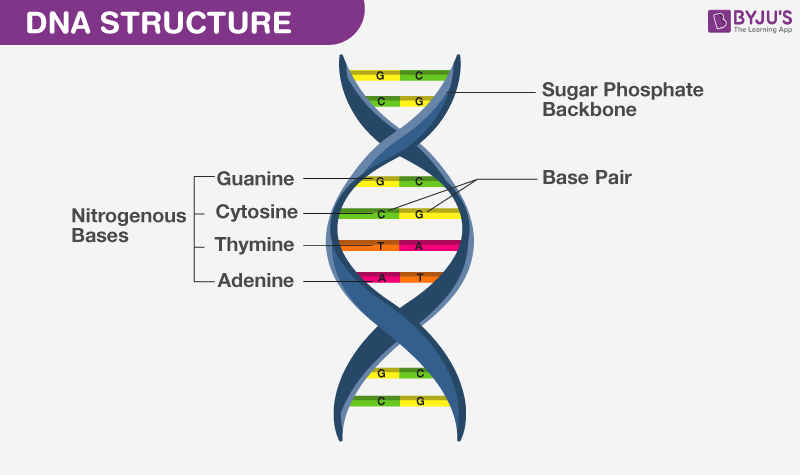
What Is Dna Meaning Dna Types Structure And Functions Dna structure dna is made up of mol ecul es cal l ed nucleot i des. e ach nucleot i de cont ai ns a phosphate group, a sugar group and a ni t rogen base. t he f our t ypes of nitrogen bases are adeni ne (a), t hymine (t ), guani ne (g ) and cyt osine (c). the order of these b ases i s what det ermines dna' s instructions, or genet i c code. Citation: pray, l. (2008) discovery of dna structure and function: watson and crick. nature education 1( 1 ) :100 the landmark ideas of watson and crick relied heavily on the work of other scientists.

Comments are closed.