Discrete Random Variable Variance Formula
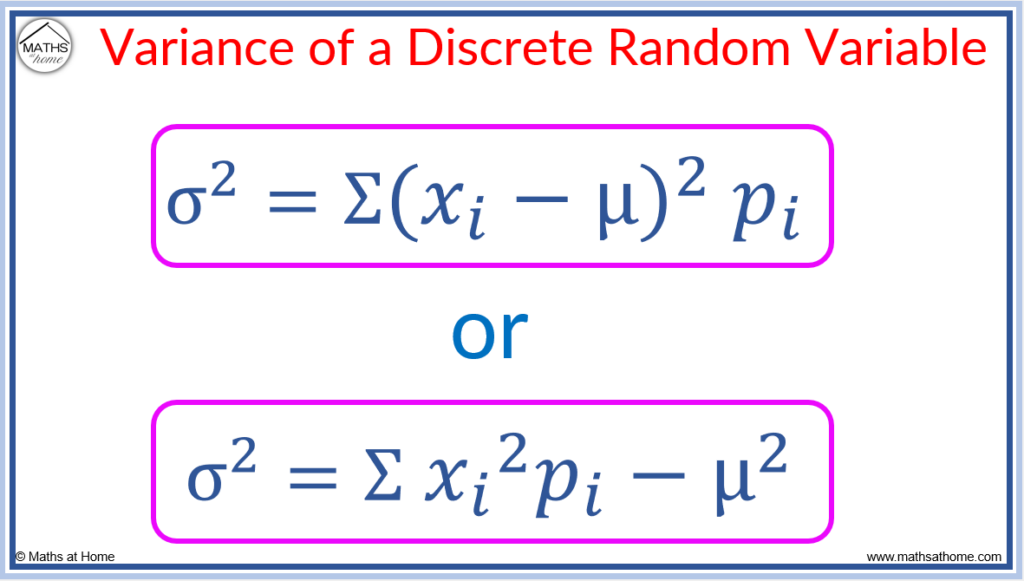
How To Calculate Variance вђ Mathsathome Definition 3.7.1. the variance of a random variable x is given by. σ2 = var(x) = e[(x − μ)2], where μ denotes the expected value of x. the standard deviation of x is given by. σ = sd(x) = √var(x). in words, the variance of a random variable is the average of the squared deviations of the random variable from its mean (expected value). The variance of a discrete random variable is given by: σ 2 = var (x) = ∑ (x i − μ) 2 f (x i) the formula means that we take each value of x, subtract the expected value, square that value and multiply that value by its probability. then sum all of those values. there is an easier form of this formula we can use.

Variance Of Discrete Random Variables Mr Mathematics This page titled 6.2: variance of discrete random variables is shared under a gnu free documentation license 1.3 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by charles m. grinstead & j. laurie snell (american mathematical society) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. The mean or expected value of a random variable can also be defined as the weighted average of all the values of the variable. the formulas for the mean of a random variable are given below: mean of a discrete random variable: e [x] = ∑xp (x = x) ∑ x p (x = x). here p (x = x) is the probability mass function. The variance of a discrete random variable, denoted by v (x), is defined to be. that is, v (x) is the average squared distance between x and its mean. variance is a measure of dispersion, telling us how “spread out” a distribution is. for our simple random variable, the variance is. Variance & standard deviation of a discrete random variable. for a given random variable x, with associated sample space s, expected value μ, and probability mass function p(x), we define the standard deviation of x, denoted sd(x) or σ, with the following: sd(x) = √∑ x ∈ s(x − μ)2 ⋅ p(x) the sum underneath the square root above.

Discrete Random Variable Variance Formula The variance of a discrete random variable, denoted by v (x), is defined to be. that is, v (x) is the average squared distance between x and its mean. variance is a measure of dispersion, telling us how “spread out” a distribution is. for our simple random variable, the variance is. Variance & standard deviation of a discrete random variable. for a given random variable x, with associated sample space s, expected value μ, and probability mass function p(x), we define the standard deviation of x, denoted sd(x) or σ, with the following: sd(x) = √∑ x ∈ s(x − μ)2 ⋅ p(x) the sum underneath the square root above. It is computed using the formula μ = Σ x p (x). the variance σ 2 and standard deviation σ of a discrete random variable x are numbers that indicate the variability of x over numerous trials of the experiment. they may be computed using the formula σ 2 = [Σ x 2 p (x)] − μ 2, taking the square root to obtain σ. Random variables can be either discrete or continuous: discrete data can only take certain values (such as 1,2,3,4,5) continuous data can take any value within a range (such as a person's height) here we looked only at discrete data, as finding the mean, variance and standard deviation of continuous data needs integration. summary.

Comments are closed.