Digestive System Histology

Histology Of The Gi Tract Lab The esophagus is a hollow muscular organ in the digestive system that connects the throat and the stomach. the esophagus has a histological structure typical of the digestive system. the inner mucosa consists of a multilayered, nonkeratinized squamous epithelium. this special epithelial layer protects the esophagus from mechanical wear and tear. Chapter 14 gastrointestinal tract. the digestive system takes in food, digests and absorbs nutrients, and eliminates the remaining waste material. the digestive system can be divided into the digestive tract (oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine) and associated digestive organs (salivary glands, pancreas.

Gastrointestinal System Overview Of Gi Histology Ditki Medical Hormones secreted by several endocrine glands, as well as endocrine cells of the pancreas, the stomach, and the small intestine, contribute to the control of digestion and nutrient metabolism. in turn, the digestive system provides the nutrients to fuel endocrine function. table 23.1 gives a quick glimpse at how these other systems contribute. Learn about the microscopic anatomy and function of the digestive system, including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. see diagrams, images, and webslides of the four layers of the gastrointestinal tract wall: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa. The histology of the entire gastrointestinal tract is largely the histology of epithelial tissues. click here for a basic introduction to epithelial tissue. the mucosal epithelium is highly differentiated along the several regions of the gi tract. at the upper and lower ends of the tract, the epithelium is protective, stratified squamous. Extending from the mouth to the anus, the digestive tract is one of the largest systems in the human body. it contains organs that regulate food intake, its digestion and absorbtion of the useful materia that it contains. in addition to this, the digestive system also eliminates the waste products from food and products from various endogenous.
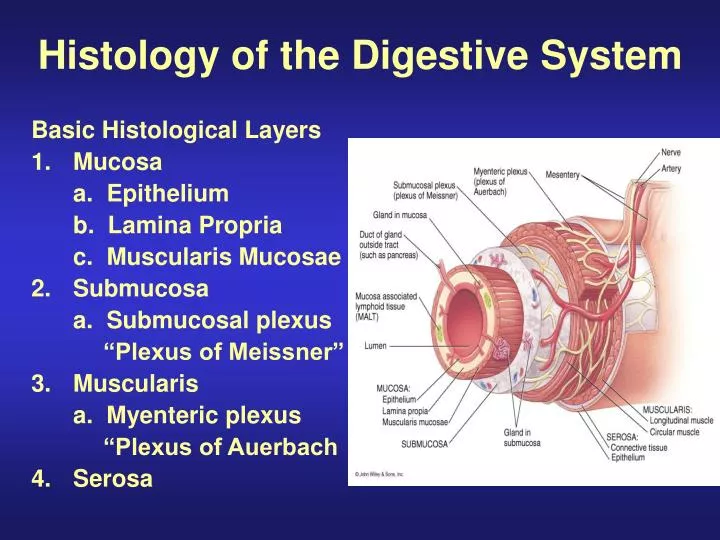
Ppt Histology Of The Digestive System Powerpoint Presentation Id The histology of the entire gastrointestinal tract is largely the histology of epithelial tissues. click here for a basic introduction to epithelial tissue. the mucosal epithelium is highly differentiated along the several regions of the gi tract. at the upper and lower ends of the tract, the epithelium is protective, stratified squamous. Extending from the mouth to the anus, the digestive tract is one of the largest systems in the human body. it contains organs that regulate food intake, its digestion and absorbtion of the useful materia that it contains. in addition to this, the digestive system also eliminates the waste products from food and products from various endogenous. Digestive system – meyers histology. this module covers the principal histological features of the alimentary canal. when you have completed viewing the images and the histological sections available of the organs of the alimentary canal you should. know the four characteristic layers of the gastro intestinal tract (gi) throughout its length. Learn about the structure and function of the digestive system, including the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas and gall bladder. explore the histological features and variations of the different tissues and organs involved in digestion.

вђњhistology Of The Digestive System Medical Illustration Anatomy And Digestive system – meyers histology. this module covers the principal histological features of the alimentary canal. when you have completed viewing the images and the histological sections available of the organs of the alimentary canal you should. know the four characteristic layers of the gastro intestinal tract (gi) throughout its length. Learn about the structure and function of the digestive system, including the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas and gall bladder. explore the histological features and variations of the different tissues and organs involved in digestion.

Comments are closed.