Data Science Statistics Levels Of Measurement

Levels Of Measurement In Statistics Albert Woods There are 4 levels of measurement: nominal: the data can only be categorized. ordinal: the data can be categorized and ranked. interval: the data can be categorized, ranked, and evenly spaced. ratio: the data can be categorized, ranked, evenly spaced, and has a natural zero. depending on the level of measurement of the variable, what you can do. Levels of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio. in statistics, we use data to answer interesting questions. but not all data is created equal. there are actually four different data measurement scales that are used to categorize different types of data: 1. nominal.

Su Lms What is level of measurement in statistics? level of measurement, also known as scale of measurement, refers to the process of categorizing data based on the characteristics and properties of the data. it’s important in statistics because it helps determine the appropriate statistical methods and tests that can be used to analyze the data. To conclude, the levels of measurement can be either qualitative or quantitative. qualitative data is split into two, as well. it can be nominal or ordinal, depending if there is any strict order or not. quantitative data also consists of 2 groups – ratios and intervals. here, the key difference is whether or not there is a true 0. The nominal level of measurement is the most fundamental form of measurement. this level categorizes or labels data without giving any quantitative value or order. it is purely qualitative and usually used for categorizing or grouping data. for example, the gender of individuals (male, female) represents nominal data. By jim frost 17 comments. the nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales are levels of measurement in statistics. these scales are broad classifications describing the type of information recorded within the values of your variables. variables take on different values in your data set. for example, you can measure height, gender, and class.
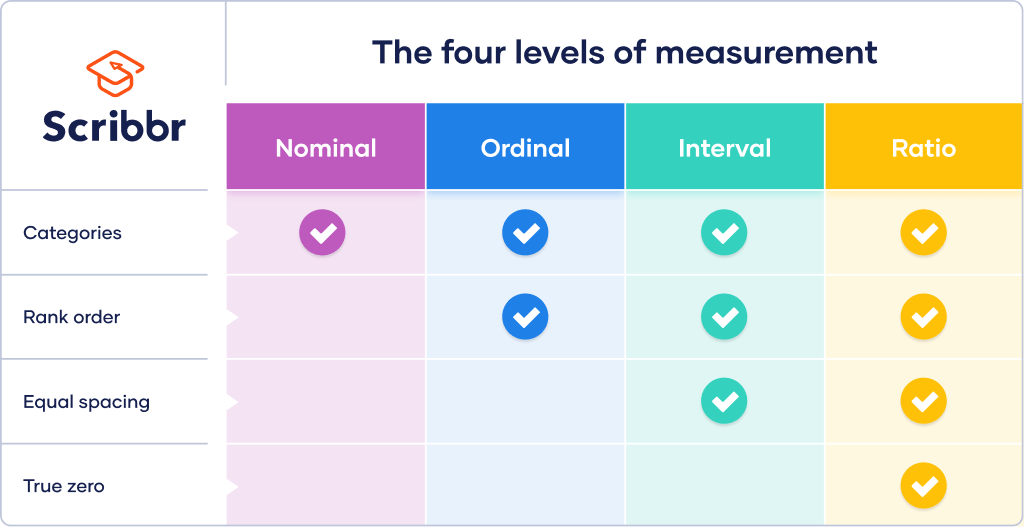
Interval Data And How To Analyze It Definitions Examples The nominal level of measurement is the most fundamental form of measurement. this level categorizes or labels data without giving any quantitative value or order. it is purely qualitative and usually used for categorizing or grouping data. for example, the gender of individuals (male, female) represents nominal data. By jim frost 17 comments. the nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales are levels of measurement in statistics. these scales are broad classifications describing the type of information recorded within the values of your variables. variables take on different values in your data set. for example, you can measure height, gender, and class. The four levels of measurement are nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio. nominal level of measurement; data at the nominal level of measurement are simply categorized or labelled into different groups categories at the most primary level. the categorisation is not ordered, let alone hierarchal. characteristics: nominal data might include qualities. The four data measurement levels, from lowest to highest, are nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. nominal data 🟨 🟩 🟦 the term “nominal” comes from latin and can be translated as “being so in name only”.
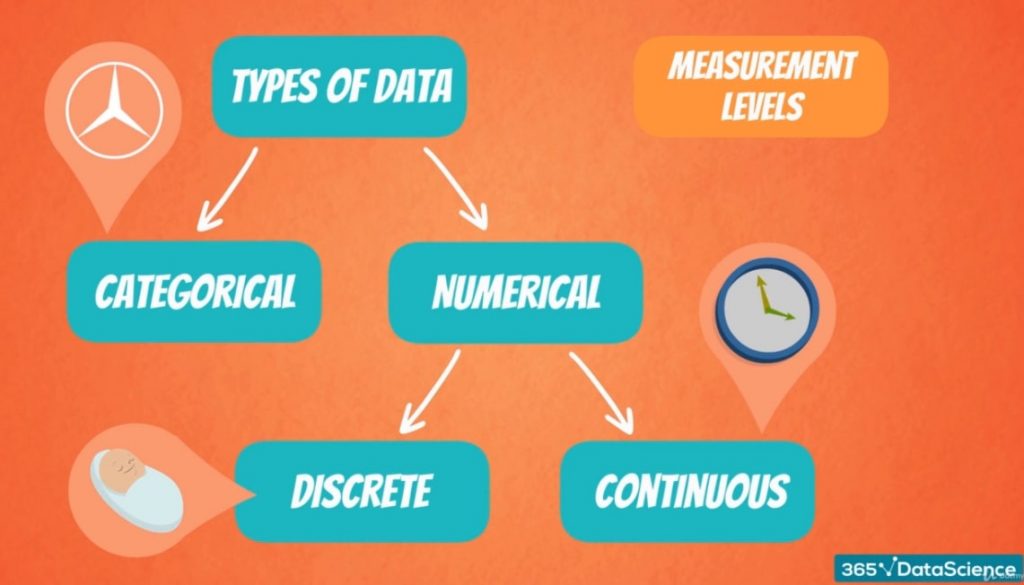
Introducing Levels Of Measurement 365 Data Science The four levels of measurement are nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio. nominal level of measurement; data at the nominal level of measurement are simply categorized or labelled into different groups categories at the most primary level. the categorisation is not ordered, let alone hierarchal. characteristics: nominal data might include qualities. The four data measurement levels, from lowest to highest, are nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. nominal data 🟨 🟩 🟦 the term “nominal” comes from latin and can be translated as “being so in name only”.

Comments are closed.