Cystic Disease Of The Kidney

Kidney Size Chart For Renal Cyst Cystic kidney disease causes cysts (sacs of fluid) to form in or around the kidneys. there are many types of cystic kidney disease. some are the result of abnormal genes; others start during fetal development or as a result of kidney failure. both adults and infants can have cystic kidney disease. A kidney cyst may become infected, causing fever and pain. a burst cyst. a kidney cyst that bursts causes severe pain in the back or side. sometimes a burst cyst may cause blood in the urine. blocked urine flow. a kidney cyst that blocks the typical flow of urine may lead to kidney swelling. these round, fluid filled pouches on or in the.

Kidney Cyst Causes Diagnosis Symptoms Complications Treatment Noninherited cystic kidney diseases include those discussed below. acquired cystic disease: this occurs in patients requiring dialysis and manifests as atrophic kidneys with microcysts. it is strongly associated with length of dialysis, and close to 100% of patients who are dialysis dependent for longer than 10 years have this condition. Cystic kidney disease is a general classification for a group of similar (heterogeneous) disorders that result in the development of cysts on the kidney. kidney cysts are abnormal sacs that can be filled with fluids, gases or solids. these pouches can be microscopic, requiring no treatment. or, they can be quite large, significantly impacting. Cystic kidney disease refers to a wide range of hereditary, developmental, and acquired conditions [1] and with the inclusion of neoplasms with cystic changes, over 40 classifications and subtypes have been identified. depending on the disease classification, the presentation may be at birth, or much later into adult life. Acquired cystic disease. multiple cysts. associated with long term dialysis, usually after > 10 years. high risk of renal cell carcinoma. cysts associated with tumors. for example, with renal cell carcinoma or nephroblastoma. solitary simple cysts. low risk of chronic kidney disease and hypertension. associated with aging.
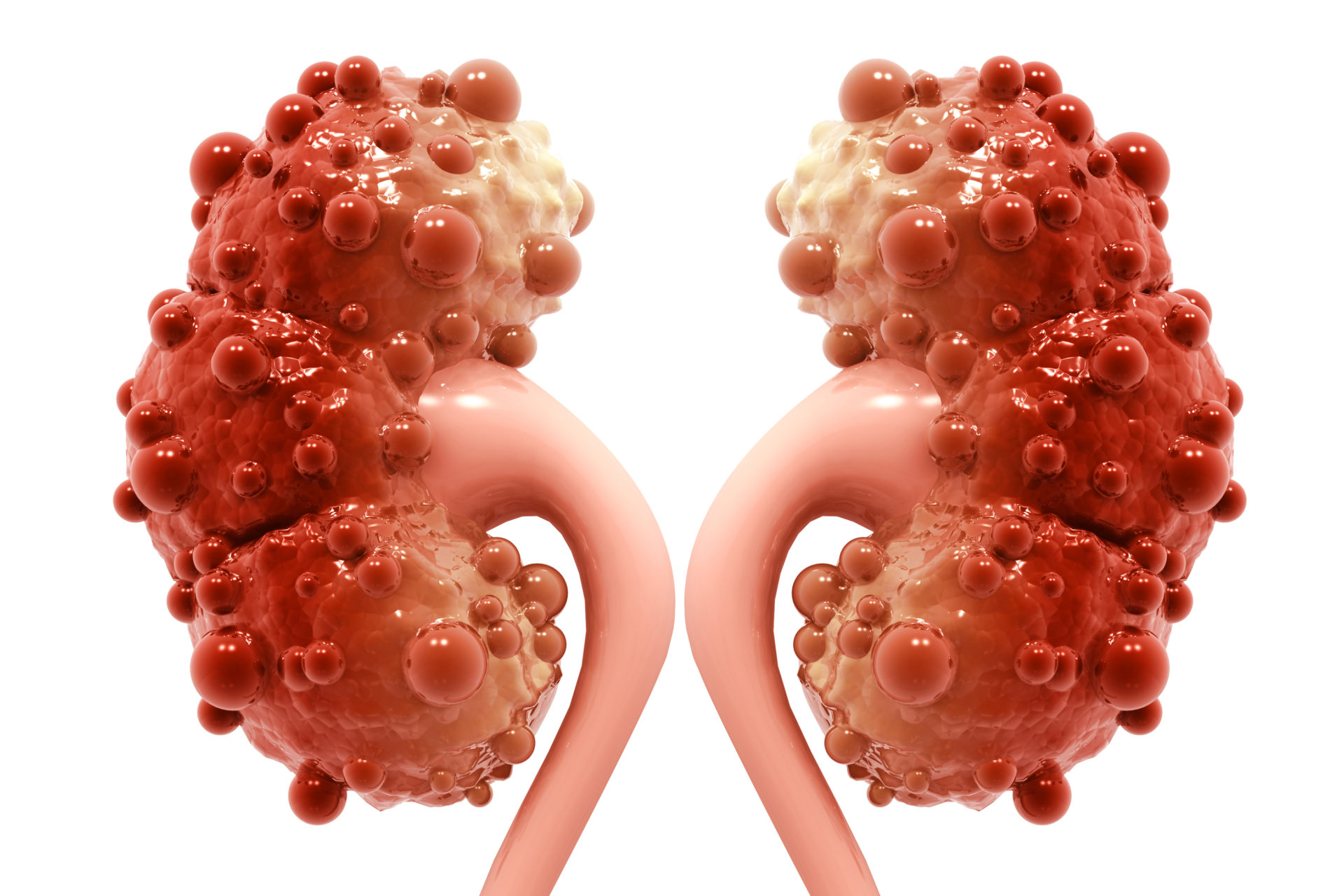
Kidney Cyst Renal Cyst Polycystic Kidney Disease Urologist Cystic kidney disease refers to a wide range of hereditary, developmental, and acquired conditions [1] and with the inclusion of neoplasms with cystic changes, over 40 classifications and subtypes have been identified. depending on the disease classification, the presentation may be at birth, or much later into adult life. Acquired cystic disease. multiple cysts. associated with long term dialysis, usually after > 10 years. high risk of renal cell carcinoma. cysts associated with tumors. for example, with renal cell carcinoma or nephroblastoma. solitary simple cysts. low risk of chronic kidney disease and hypertension. associated with aging. Acquired cystic kidney disease occurs in children and adults who have. chronic kidney disease (ckd) —a condition that develops over many years and may lead to end stage kidney disease, or esrd. the kidneys of people with ckd gradually lose their ability to filter wastes, extra salt, and fluid from the blood properly. Polycystic kidney enlarge image. polycystic kidney disease (pkd) is a condition in which clusters of cysts grow in the body, mainly in the kidneys. over time, the cysts may cause the kidneys to get bigger and stop working. pkd is most often passed through families. this is called an inherited condition.

Comments are closed.