Consumer Surplus Explained A Level Ib Economics
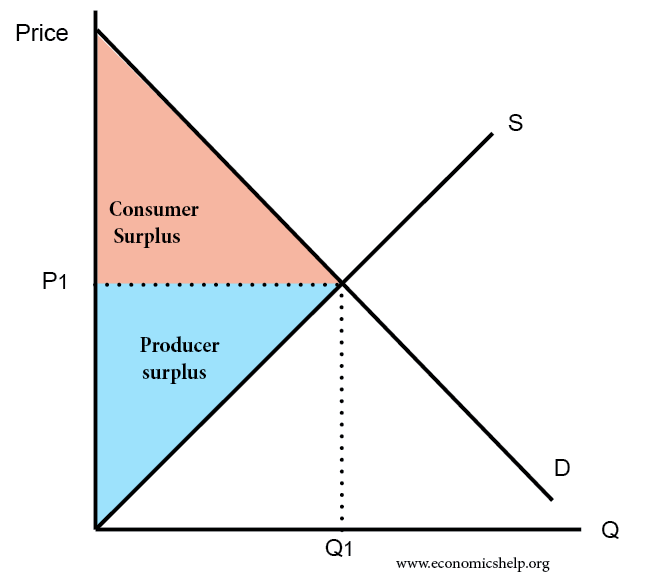
Definition Of Consumer Surplus Economics Help The concept of consumer surplus as an important measure of economic welfare is covered in this short revision video.#aqaeconomics #ibeconomics #edexceleconomics. What is consumer surplus? when there is a difference between the price that you pay in the market and the value that you place on the product, then the concept of consumer surplus becomes a useful one to look at. this is an important idea that you can use on many occasions in your exams. exam question on changes in consumer and producer surplus.

Explaining Consumer Surplus Economics Tutor2u Definition: consumer surplus is the difference between what the consumer was willing and able to pay (the demand curve) for a good or a service and what he actually paid (the market price). to explain this concept we will use the diagram above and an example – beer. chris is a university student and he likes going out on fridays. Consumer surplus is the difference between the total amount that consumers are willing and able to pay for a good or service (shown by the demand curve) and the total amount they actually do pay (i.e. the market price). consumer surplus is indicated by the area under the demand curve and above the market price. share : economics. Free a level economics study buddy. consumer surplus is the difference between the price consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and the market price. producer surplus is the difference between the price that producers are willing to sell for and the market price. both consumer and producer surplus can be shown on the demand. Allocative efficiency happens when competitive market is in equilibrium, where resources are allocated in the most efficient way from society’s point of view. social surplus (consumer producer surplus) is maximized. marginal social benefit = marginal social cost. « previous. next ». ib economics notes on 1.6 market efficiency.

Explaining Consumer Surplus Tutor2u Economics Free a level economics study buddy. consumer surplus is the difference between the price consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and the market price. producer surplus is the difference between the price that producers are willing to sell for and the market price. both consumer and producer surplus can be shown on the demand. Allocative efficiency happens when competitive market is in equilibrium, where resources are allocated in the most efficient way from society’s point of view. social surplus (consumer producer surplus) is maximized. marginal social benefit = marginal social cost. « previous. next ». ib economics notes on 1.6 market efficiency. Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. Consumer surplus always decreases when a binding price floor is instituted in a market above the equilibrium price. the total economic surplus equals the sum of the consumer and producer surpluses. price helps define consumer surplus, but overall surplus is maximized when the price is pareto optimal, or at equilibrium.
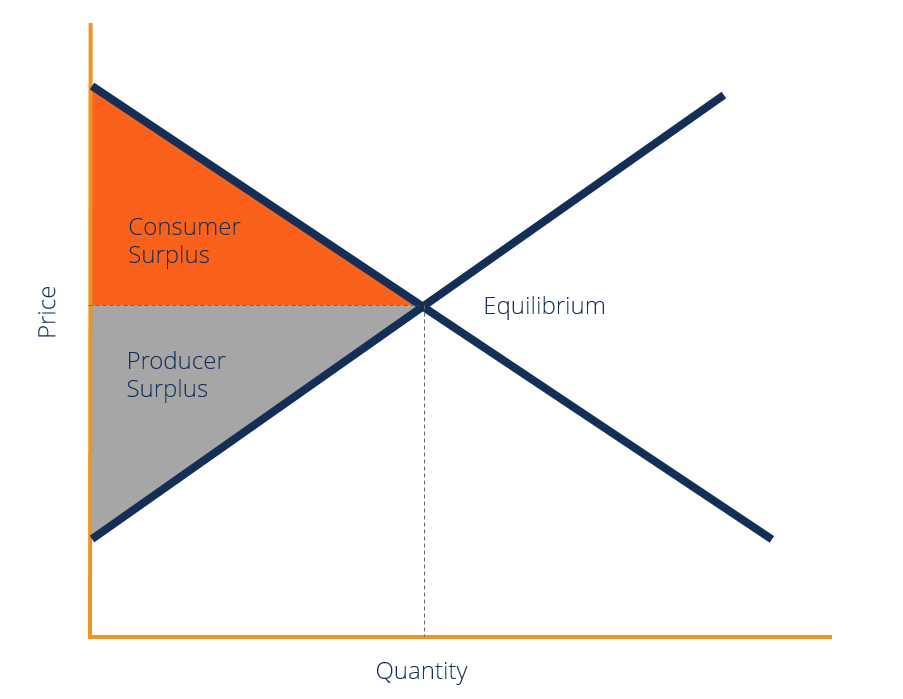
Consumer Surplus Formula Guide Examples How To Calculate Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. Consumer surplus always decreases when a binding price floor is instituted in a market above the equilibrium price. the total economic surplus equals the sum of the consumer and producer surpluses. price helps define consumer surplus, but overall surplus is maximized when the price is pareto optimal, or at equilibrium.

Explaining Consumer Surplus Tutor2u Economics

Comments are closed.