Consumer S Equilibrium Utility Analysis вђ Tutor S Tips

Consumer S Equilibrium Utility Analysis вђ Tutor S Tips Assumptions of consumer’s equilibrium under utility analysis : rational consumer: consumer should be rational who is keen to get maximum satisfaction out of his limited income. cardinal utility: utility is measured in terms of cardinal numbers such as 1,2,3 etc. Please check out our full article: tutorstips consumers equilibrium utility analysis ! our website link ! tutorstips h.

Consumer S Equilibrium Utility Analysis вђ Tutor S Tips Advertisement. the main difference between utility analysis and indifference curve analysis is that in utility analysis, the consumer behaviour is discussed with the commodities independent of each other whereas, in indifference curve analysis, the commodities can be the substitute, complementary and unrelated goods. advertisement. उपयोगिता विश्लेषण के तहत उपभोक्ता के संतुलन का अनुमान (assumptions of consumer’s equilibrium under utility analysis): उपभोक्ता के संतुलन का निर्धारण (determination of consumer’s equilibrium): 1. Substitution effect on consumer equilibrium. in fig, the quantities purchased of coca cola and pepsi are shown on x axis and y axis respectively. ab is the original budget line with an income level of rs.200 and ic 1 is the original indifference curve. here, the consumer is equilibrium at point e, by getting 6 units of pepsi and 2 units of coca. The above explanation of a consumer’s equilibrium has been given with the help of the concept of utility; it is, therefore, called the analysis of demand or consumer’s behaviour. modern economists explain consumer’s equilibrium with the help of indifference curves referred to below in appendix. shortcomings of the utility analysis:.
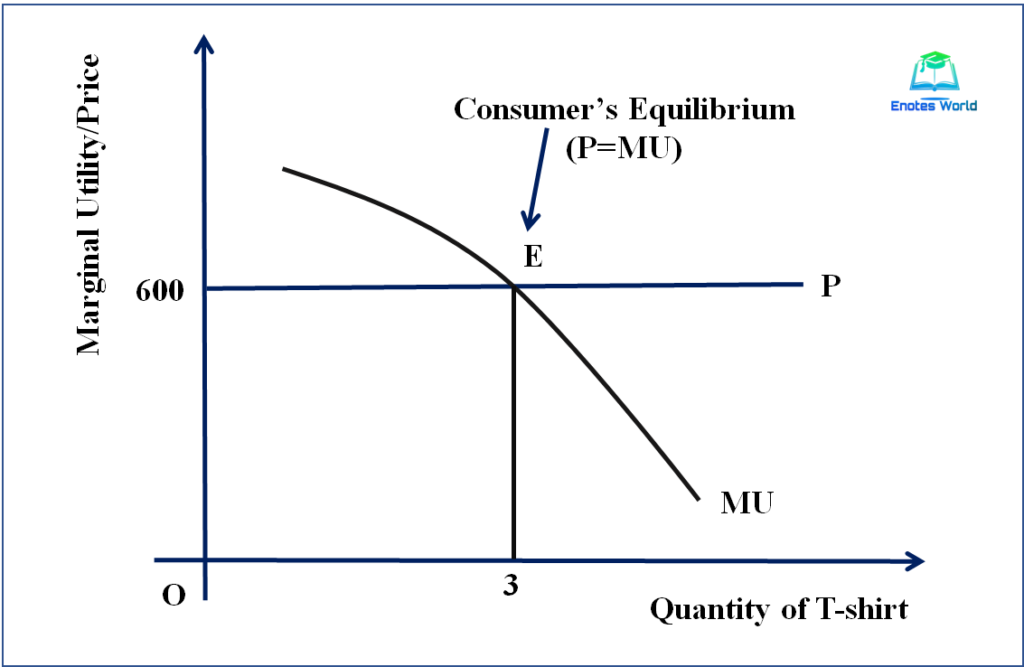
юааconsumerюабтащюааsюаб юааequilibriumюаб Under Cardinal юааutilityюаб юааanalysisюаб Microeconomic Substitution effect on consumer equilibrium. in fig, the quantities purchased of coca cola and pepsi are shown on x axis and y axis respectively. ab is the original budget line with an income level of rs.200 and ic 1 is the original indifference curve. here, the consumer is equilibrium at point e, by getting 6 units of pepsi and 2 units of coca. The above explanation of a consumer’s equilibrium has been given with the help of the concept of utility; it is, therefore, called the analysis of demand or consumer’s behaviour. modern economists explain consumer’s equilibrium with the help of indifference curves referred to below in appendix. shortcomings of the utility analysis:. There is no problem with the consumer’s expenditure, i.e., he has only sufficient money to buy whatever quantity he decides to buy to achieve his own goal. consumer equilibrium formula. the formula for consumer's equilibrium is as follows: consumer’s surplus = total utility obtained – total expenditure (at the consumer's equilibrium point). Microeconomics seeks to understand the behavior of individual economic agents such as individuals and businesses. economists believe that we can analyze individuals’ decisions, such as what goods and services to buy, as choices we make within certain budget constraints. generally, consumers are trying to get the most for their limited budget.

Comments are closed.