Consumer S Equilibrium In Case Of Two Commodity Model By Shiv Kumar
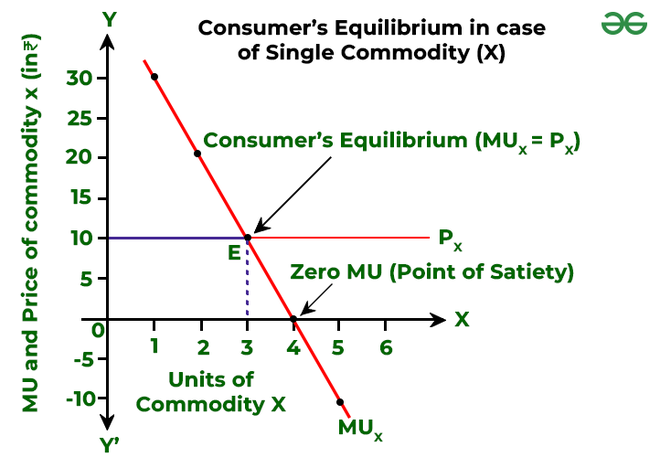
Consumer S Equilibrium In Case Of Single And Two Commodity Geeks This combination will provide maximum satisfaction to consumers (or state of equilibrium) because a rupee worth of mu in case of commodity x is 5 ( mux px = 10 2 = 5) and in the case of commodity y is also 5. ( muy py = 15 3 = 5) (= marginal utility (mu) of the last rupee spent on each good). it is important to note that maximum satisfaction of. The consumer will be in the state of equilibrium when the marginal utility of commodity x (in terms of rupees) is equal to the price of commodity x. 2. the marginal utility can never be negative. 3. if mux px > muy py, then the consumer must buy more of commodity y and less of commodity x to reach equilibrium.

Consumer S Equilibrium In Case Of Two Commodity Model By Shiv Kumar 12th economics. Microeconomics: consumer's equilibriumconsumer's equilibrium in two commodity caseconsumer's equilibrium in case of two commodityqns. when does a consumer be. Gossen’s second law in the real world, a consumer purchases more than one commodity. let us assume that a consumer purchases two goods x and y. how does a consumer spend his fixed money income in purchasing two goods so as to maximize his total utility? the law of equi marginal utility tells us the way how a consumer maximizes his total. Utility. consumer satisfaction. utility is the want satisfying power of the commodity. there is no standard unit for measuring utility but economists used imaginary units called utils to measure it. there are two approaches to studying consumer equilibrium: 1) cardinal approach. 2) ordinal approach.
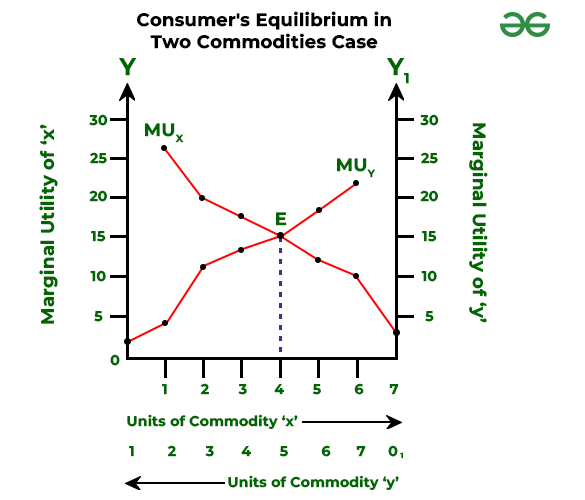
Consumer S Equilibrium In Case Of Single And Two Commodity Geeks Gossen’s second law in the real world, a consumer purchases more than one commodity. let us assume that a consumer purchases two goods x and y. how does a consumer spend his fixed money income in purchasing two goods so as to maximize his total utility? the law of equi marginal utility tells us the way how a consumer maximizes his total. Utility. consumer satisfaction. utility is the want satisfying power of the commodity. there is no standard unit for measuring utility but economists used imaginary units called utils to measure it. there are two approaches to studying consumer equilibrium: 1) cardinal approach. 2) ordinal approach. 1. marginal utility of the last rupee spent on each good is the same. 2. marginal utility of a commodity falls as more of it is consumed. let us understand the consumer’s equilibrium in the case of two commodities with an example. suppose a consumer has to spend ₹. 24 on two commodities i.e. x and y. Figure 4: price on consumer equilibrium. in figure 4.14, the drop in the price of commodity x is denoted by the corresponding shifts of budget line from ab1 to ab2, ab2 to ab3 and ab3 to ab4. c1, c2, c3, and c4 represent a shift in consumer’s equilibrium. as the price of commodity x decreases, the consumer’s real income increases.

Comments are closed.