Consumer Equilibrium Meaning Example And Graph Efinancem
Consumer Equilibrium Meaning Example And Graph Efinancem Consumer equilibrium is a very popular economics concept. this is because it helps to explain how consumers maximize their utility by consuming one or more commodities. moreover, it also assists consumers in ranking the combination of two or more commodities on the basis of their taste and preference. table of contents. 1. marginal utility of the last rupee spent on each good is the same. 2. marginal utility of a commodity falls as more of it is consumed. let us understand the consumer’s equilibrium in the case of two commodities with an example. suppose a consumer has to spend ₹. 24 on two commodities i.e. x and y.
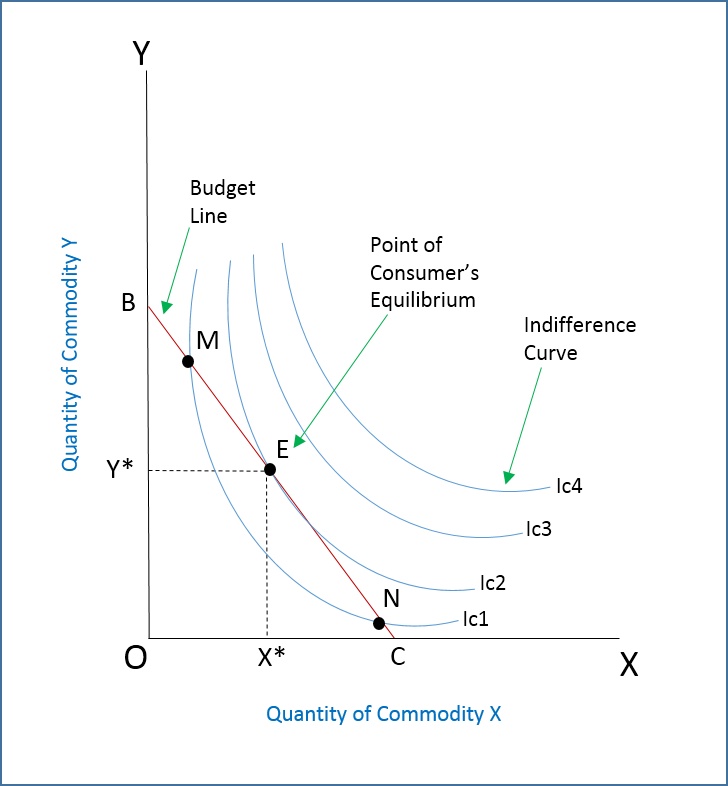
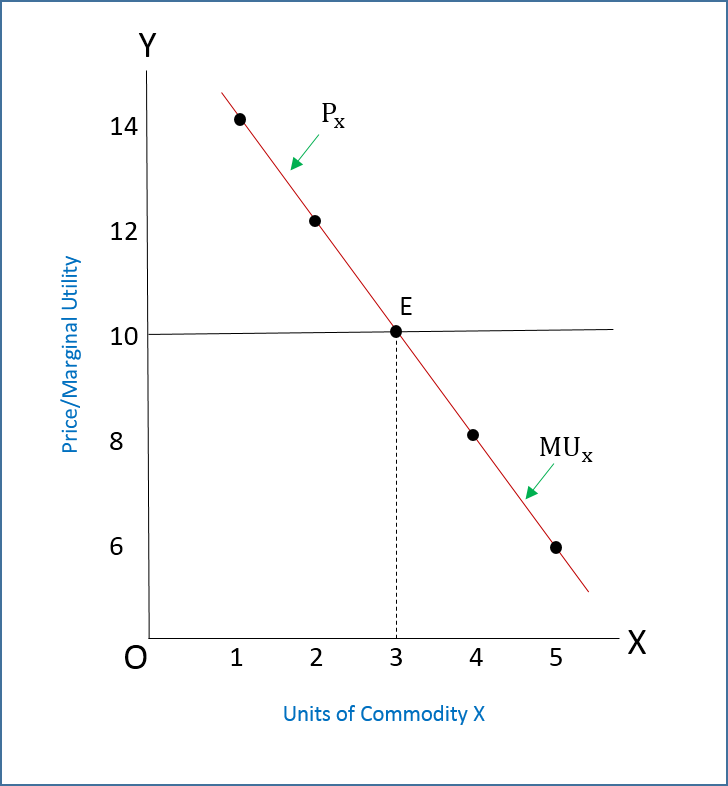
Consumer Equilibrium Meaning Example And Graph Efinancem The slope of budget line is given as: oa ob = p x p y. at point e where mrs y,x = p x p y. therefore, the consumer is at equilibrium at point e. as the ic2 curve is tangent to the budget line ab, ic2 is the highest indifference curve that a consumer can attain at the given income level and market price of commodities. However, p = mu is a necessary but not a sufficient condition for a consumer’s equilibrium. in fig. 4, we find that the mu curve is intersecting the price curve pp at two different points m and n. so far m is concerned, although by having oa quantity the consumer is reaching the point where p – mu but it is not equilibrium. Course: ap®︎ college macroeconomics > unit 1. lesson 6: market equilibrium, disequilibrium, and changes in equilibrium. market equilibrium. changes in market equilibrium. changes in equilibrium price and quantity when supply and demand change. lesson summary: market equilibrium, disequilibrium, and changes in equilibrium. Lesson 3: market equilibrium and changes in equilibrium. market equilibrium. market equilibrium. changes in market equilibrium. changes in equilibrium price and quantity when supply and demand change. changes in equilibrium price and quantity: the four step process. lesson summary: market equilibrium, disequilibrium, and changes in equilibrium.
Consumer Equilibrium Meaning Example And Graph Efinancem Course: ap®︎ college macroeconomics > unit 1. lesson 6: market equilibrium, disequilibrium, and changes in equilibrium. market equilibrium. changes in market equilibrium. changes in equilibrium price and quantity when supply and demand change. lesson summary: market equilibrium, disequilibrium, and changes in equilibrium. Lesson 3: market equilibrium and changes in equilibrium. market equilibrium. market equilibrium. changes in market equilibrium. changes in equilibrium price and quantity when supply and demand change. changes in equilibrium price and quantity: the four step process. lesson summary: market equilibrium, disequilibrium, and changes in equilibrium. Consumer equilibrium meaning. consumer equilibrium is like finding the perfect balance when spending money on things you like to maximize satisfaction. it’s about getting the most happiness from your purchases with your current income without feeling the need to change what you’re buying. it considers your preferences, budget, and prices of. Consumer’s equilibrium means a state of maximum satisfaction. a situation where a consumer spends his given income purchasing one or more commodities so that he gets maximum satisfaction and has no urge to change this level of consumption, given the prices of commodities, is known as the consumer’s equilibrium. the marginal utility of.
.bmp)
What Is Consumer Equilibrium Consumer equilibrium meaning. consumer equilibrium is like finding the perfect balance when spending money on things you like to maximize satisfaction. it’s about getting the most happiness from your purchases with your current income without feeling the need to change what you’re buying. it considers your preferences, budget, and prices of. Consumer’s equilibrium means a state of maximum satisfaction. a situation where a consumer spends his given income purchasing one or more commodities so that he gets maximum satisfaction and has no urge to change this level of consumption, given the prices of commodities, is known as the consumer’s equilibrium. the marginal utility of.

Comments are closed.