Congenital Anomalies Of Lungs Pulmonary Hypoplasia

Congenital Lung Diseases Dr Ankit Parakh Pulmonary hypoplasia is a relatively uncommon medical condition characterized by incomplete development of the lungs that can affect the overall development of the child. it can be either primary (idiopathic) or secondary to other congenital anomalies and usually leads to severe respiratory insufficiency in the fetus. Pulmonary hypoplasia is a condition where a fetus or baby’s lungs haven’t developed as expected. it can be present at birth or detected on an ultrasound during pregnancy. it’s almost always caused by an underlying health condition like congenital diaphragmatic hernia or low levels of amniotic fluid. contents overview symptoms and causes.
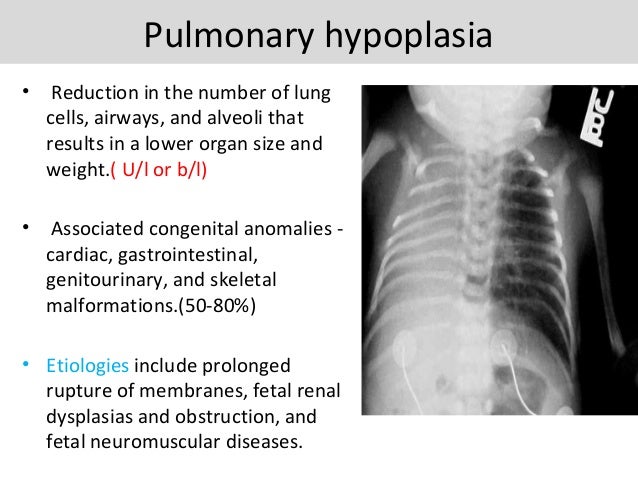
Development Of Lung Congenital lung abnormalities are being detected more frequently at routine high resolution prenatal ultrasonography. the most commonly encountered anomalies include lung agenesis hypoplasia complex (pulmonary underdevelopment), congenital pulmonary airway malformations, congenital lobar overinflation, bronchial atresia, bronchogenic cysts, congenital high airway obstruction syndrome, scimitar. Pulmonary hypoplasia is a condition characterized by small, underdeveloped lungs that can affect not only breathing but also heart function, ability to feed, hearing and overall development. some children with pulmonary hypoplasia develop a related condition known as pulmonary hypertension, which causes high blood pressure in the arteries of. In pulmonary hypoplasia, the lung consists of incompletely developed lung parenchyma connected to underdeveloped bronchi. besides disturbances of the bronchopulmonary vasculature, there is a high incidence (approximately 50 85%) of associated congenital anomalies such as cardiac, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, and skeletal malformations. Pathology. pulmonary hypoplasia is characterized by disproportionately low lung volume and weight with consequent reduced gas exchange. however lung weight can be increased by edema and congestion and so histological features such as low alveolar count, reduced branching of airways, fewer, smaller vessels and low dna content are helpful findings.

Comments are closed.