Concepts In Protein Structure
/protein-structure-373563_final11-5c81967f46e0fb00012c667d.png)
Four Types Of Protein Structure In fact, the term protein sequence is often used interchangeably with primary structure. in 1973, chris anfinsen demonstrated that the primary amino sequence of a protein uniquely determines the higher orders of structure for a protein and is thus of fundamental importance (anfinsen, 1973). it is noteworthy, however, that changes in the local. A. domains. a structural domain is an element of the protein's overall structure that is stable and often folds independently of the rest of the protein chain. like the ph domain above, many domains are not unique to the protein products of one gene, but instead appear in a variety of proteins. proteins sharing more than a few common domains.
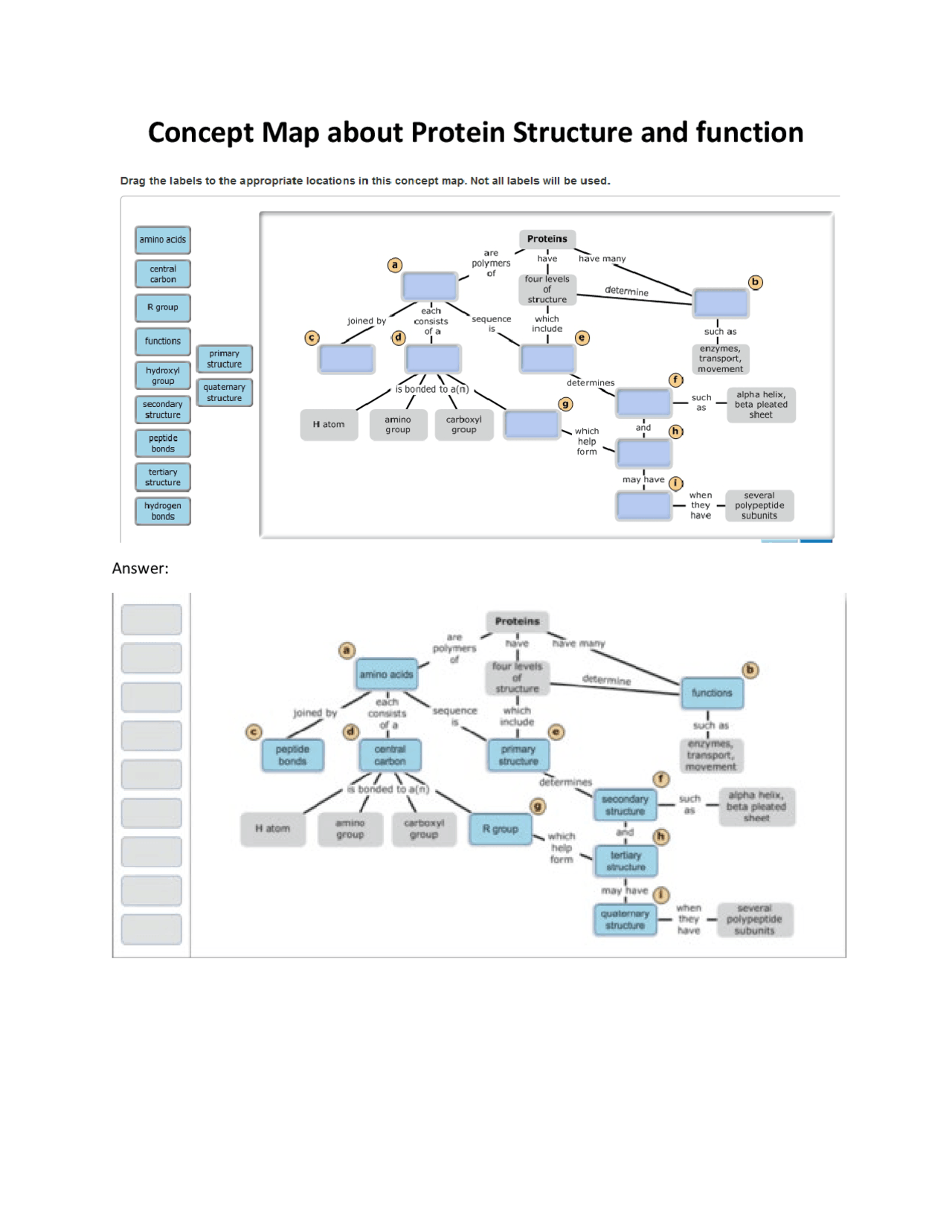
Concept Map About Protein Structure And Function Docsity The linear sequence of amino acids within a protein is considered the primary structure of the protein. proteins are built from a set of only twenty amino acids, each of which has a unique side. Proteins are polypeptide structures consisting of 1 or more long chains of amino acid residues. they perform various organism functions, including dna replication, transporting molecules, catalyzing metabolic reactions, and providing cell structural support. a protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary. We shall examine protein structure at four distinct levels (figure 2.17) 1) how sequence of the amino acids in a protein (primary structure) gives identity and characteristics to a protein (figure 2.18); 2) how local interactions between one part of the polypeptide backbone and another affect protein shape (secondary structure); 3) how the. The 3d structure of a protein is referred to as its tertiary structure and is made by further folding of secondary proteins. interactions between the side chains of amino acids lead to the formation of the tertiary structure, and bonds form between them as the protein folds. these include hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and disulfide bonds.
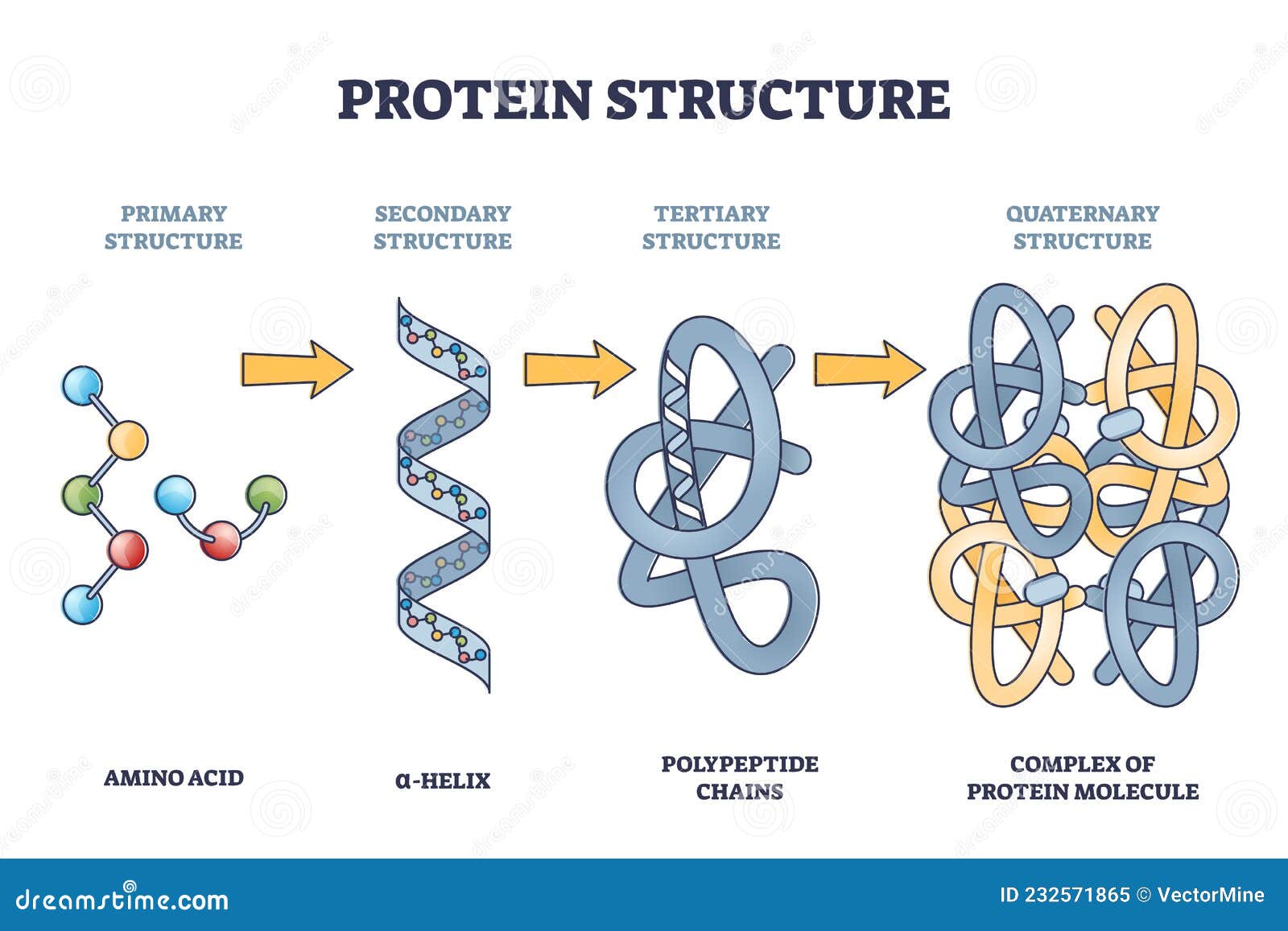
Protein Structure Levels From Amino Acid To Complex Molecule Outline We shall examine protein structure at four distinct levels (figure 2.17) 1) how sequence of the amino acids in a protein (primary structure) gives identity and characteristics to a protein (figure 2.18); 2) how local interactions between one part of the polypeptide backbone and another affect protein shape (secondary structure); 3) how the. The 3d structure of a protein is referred to as its tertiary structure and is made by further folding of secondary proteins. interactions between the side chains of amino acids lead to the formation of the tertiary structure, and bonds form between them as the protein folds. these include hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and disulfide bonds. Protein structure is the three dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid chain molecule. proteins are polymers – specifically polypeptides – formed from sequences of amino acids, which are the monomers of the polymer. a single amino acid monomer may also be called a residue, which indicates a repeating unit of a polymer. The three dimensional structure of a protein is determined by its amino acid sequence. the function of protein depends on its structure. an isolated protein has a unique or nearly unique structure. the most important forces stabilizing the specific structure of a protein are non covalent interactions.
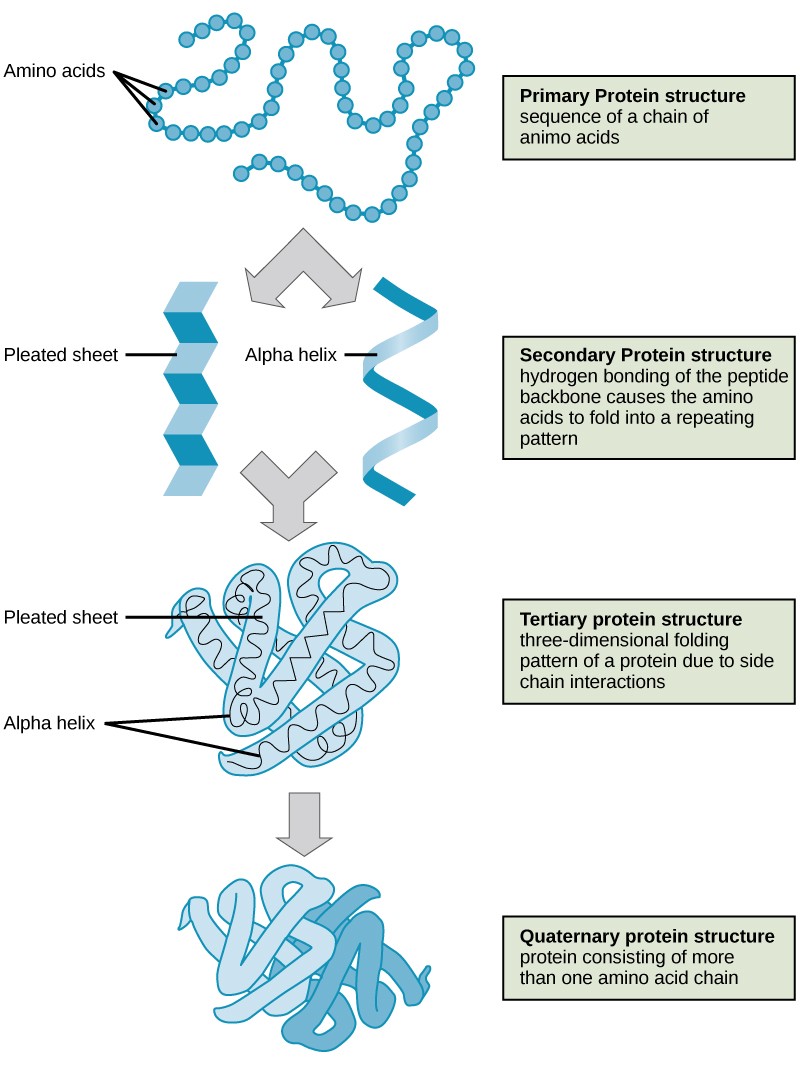
Chapter 3 Amino Acids Proteins вђ Introduction To Molecular And Cell Protein structure is the three dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid chain molecule. proteins are polymers – specifically polypeptides – formed from sequences of amino acids, which are the monomers of the polymer. a single amino acid monomer may also be called a residue, which indicates a repeating unit of a polymer. The three dimensional structure of a protein is determined by its amino acid sequence. the function of protein depends on its structure. an isolated protein has a unique or nearly unique structure. the most important forces stabilizing the specific structure of a protein are non covalent interactions.

Protein Concept Map Template Edrawmind

Comments are closed.