Chaperones Functions Types

Chaperones Functions Types Youtube Chaperones are a family of proteins that play a vital role in the stabilization of unfolded proteins. and each possesses different functions. example of chaperon proteins are the “heat shock. The first molecular chaperones discovered were a type of assembly chaperones which assist in the assembly of nucleosomes from folded histones and dna. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] one major function of molecular chaperones is to prevent the aggregation of misfolded proteins, thus many chaperone proteins are classified as heat shock proteins , as the tendency.
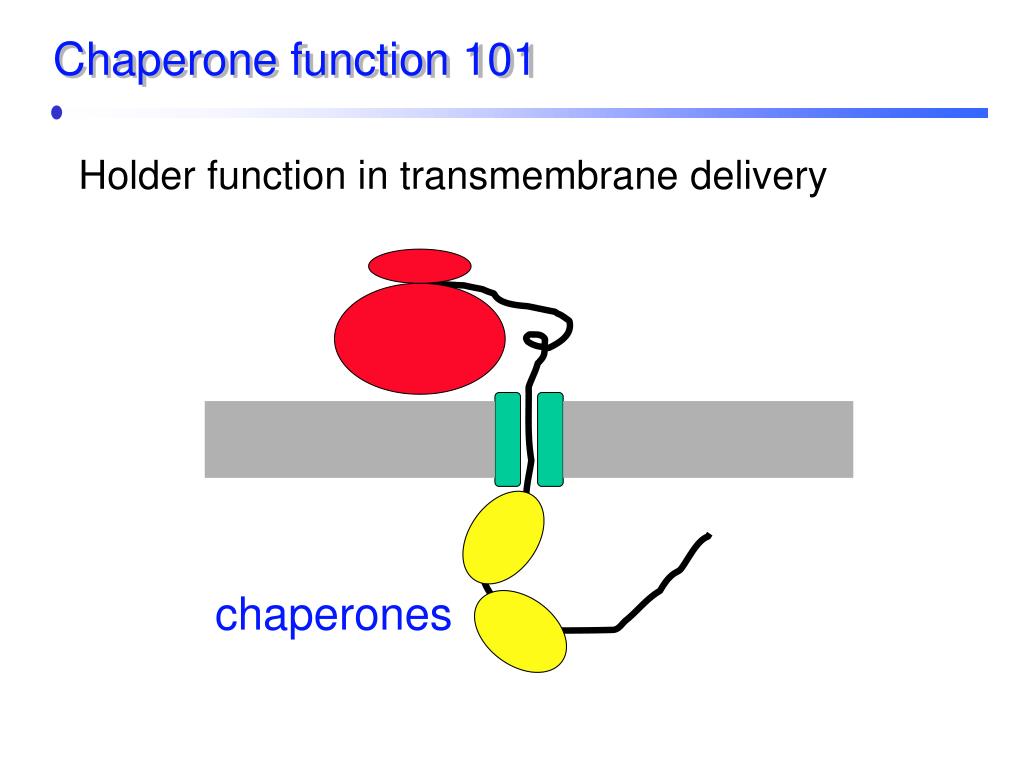
Ppt Chaperones And Protein Folding Powerpoint Presentation Free The fundamental roles and impact of core chaperones. a the functional roles of the 32 core chaperones. chaperones with several functions appear in all categories that apply. core chaperones performed basic function required by different cell types. Core chaperones performed basic function required by different cell types. b the overlap between core chaperones (top) or variable chaperones (bottom), and chaperones with known aberrations that. Understanding chaperone function at the atomic level, and in particular its mode of interaction with client proteins, is crucial to understanding the fundamental roles chaperones play in biology. this book fills a gap in the literature by comprehensively summarizing and discussing new advanced experimental techniques for their analysis. Further experimentation revealed several types of functions for different chaperone proteins, which may be attributed to the diversity of their structures. current structural information divides the chaperones into five major classes based on their observed molecular weights: hsp60, hsp70, hsp90, hsp104, and the small hsps.

Ppt Chaperones And Protein Folding Powerpoint Presentation Free Understanding chaperone function at the atomic level, and in particular its mode of interaction with client proteins, is crucial to understanding the fundamental roles chaperones play in biology. this book fills a gap in the literature by comprehensively summarizing and discussing new advanced experimental techniques for their analysis. Further experimentation revealed several types of functions for different chaperone proteins, which may be attributed to the diversity of their structures. current structural information divides the chaperones into five major classes based on their observed molecular weights: hsp60, hsp70, hsp90, hsp104, and the small hsps. The diverse functions of chaperones are achieved through their interaction with target proteins, altering protein conformation and function. several classes of chaperones exist (as reviewed by nose and chakrabarti [2]). the main class of chaperones is heat shock proteins (hsps), which are primarily upregulated during stress conditions in which. Circled c, molecular chaperone; 1, mobile chaperone in the cytosol; 2, chaperone inside an organelle, such as the nucleus or a mitochondrion; 3, sessile chaperone anchored to a particle (e.g., ribosome) in the cytosol; 4 and 5, sessile chaperone anchored to the cell membrane on the cytosolic side (4) or on the outside in the extracellular space.

1 Schematic Representation Of The Functioning Of Chaperone Cycle Steps The diverse functions of chaperones are achieved through their interaction with target proteins, altering protein conformation and function. several classes of chaperones exist (as reviewed by nose and chakrabarti [2]). the main class of chaperones is heat shock proteins (hsps), which are primarily upregulated during stress conditions in which. Circled c, molecular chaperone; 1, mobile chaperone in the cytosol; 2, chaperone inside an organelle, such as the nucleus or a mitochondrion; 3, sessile chaperone anchored to a particle (e.g., ribosome) in the cytosol; 4 and 5, sessile chaperone anchored to the cell membrane on the cytosolic side (4) or on the outside in the extracellular space.

Comments are closed.