Calculating Formal Charge Lewis Structure Craftukraine
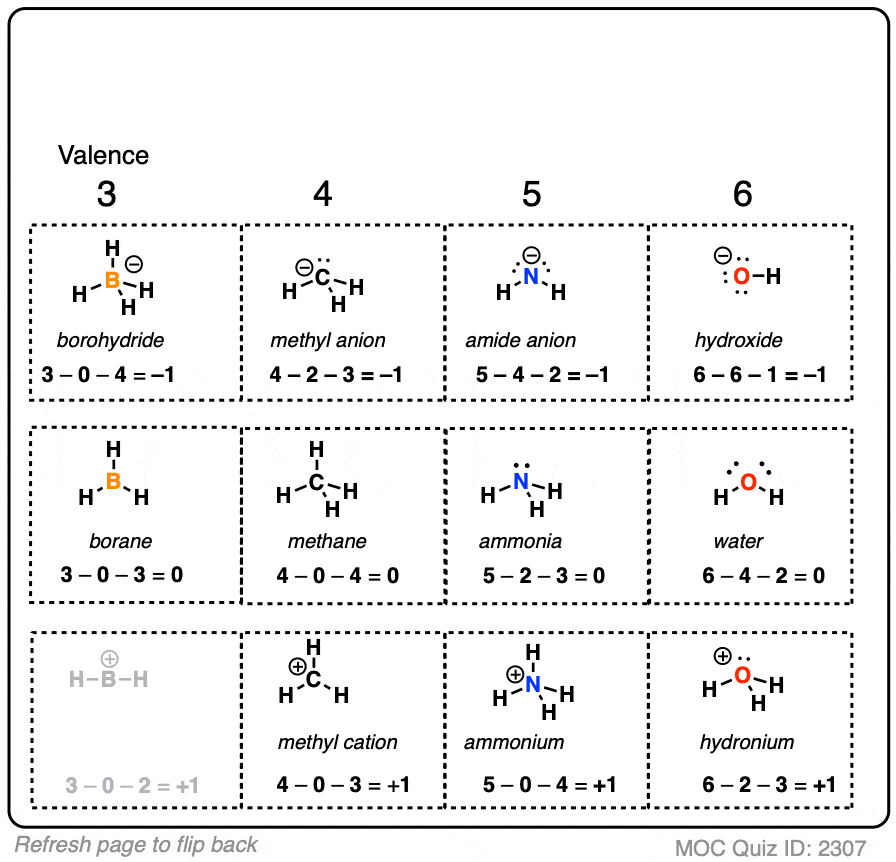
Calculating Formal Charge Lewis Structure Craftukraine To find formal charges in a lewis structure, for each atom, you should count how many electrons it "owns". count all of its lone pair electrons, and half of its bonding electrons. the difference between the atom's number of valence electrons and the number it owns is the formal charge. for example, in nh 3, n has 1 lone pair (2 electrons) and 3. A step by step description on how to calculate formal charges. formal charges are important because they allow us to predict which lewis structure is the mo.

Calculating Formal Charge Lewis Structure Craftukraine 1. formal charge. formal charge is a book keeping formalism for assigning a charge to a specific atom to obtain the formal charge of an atom, we start by counting the number of valence electrons [note 1] for the neutral atom, and then subtract from it the number of electrons that it “owns” (i.e. electrons in lone pairs, or singly occupied orbitals) and half of the electrons that it. Formal charges are not real charges, they are a way of looking at electron distributions in a lewis dot structure. in section 8.7 we will cover electronegativty and molecular polarity, and then we will look at the actual charge distribution in real molecules, which does not always reflect the formal charge distribution. Using formal charges to distinguish between lewis structures. as an example of how formal charges can be used to determine the most stable lewis structure for a substance, we can compare two possible structures for co 2. both structures conform to the rules for lewis electron structures. An atom can have the following charges: positive, negative, or neutral, depending on the electron distribution. this is often useful for understanding or predicting reactivity. identifying formal charges helps you keep track of the electrons. the formal charge is the charge on the atom in the molecule. the term “formal” means that this.
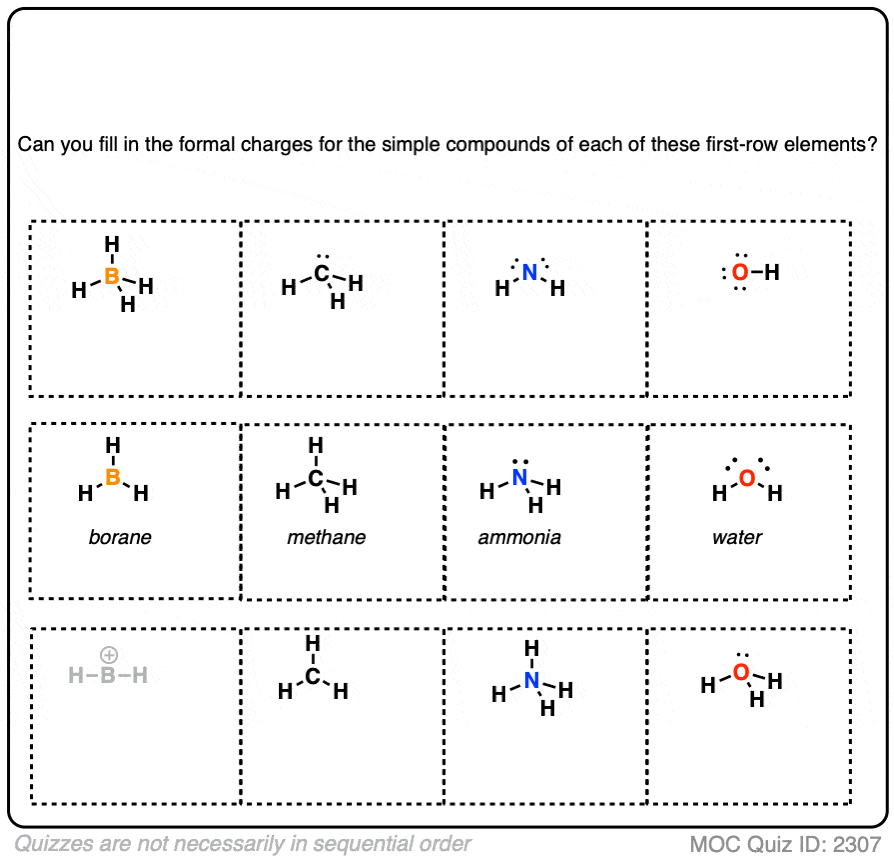
Calculating Formal Charge Lewis Structure Craftukrain Vrogue Co Using formal charges to distinguish between lewis structures. as an example of how formal charges can be used to determine the most stable lewis structure for a substance, we can compare two possible structures for co 2. both structures conform to the rules for lewis electron structures. An atom can have the following charges: positive, negative, or neutral, depending on the electron distribution. this is often useful for understanding or predicting reactivity. identifying formal charges helps you keep track of the electrons. the formal charge is the charge on the atom in the molecule. the term “formal” means that this. Calculating formal charge from lewis structures assign formal charges to each atom in the interhalogen ion icl 4 −. icl 4 −. solution. step 1. we divide the bonding electron pairs equally for all i–cl bonds: step 2. we assign lone pairs of electrons to their atoms. each cl atom now has seven electrons assigned to it, and the i atom has. Formal charge is based on lewis structure. only covalent bonds have formal charges. formal charge calculation example. as an example, let's calculate the formal charges for carbon dioxide. remember, carbon dioxide has a central carbon double bonded to two oxygens. let's start with the formal charge of the oxygen atoms. oxygen is in group six.

Calculating Formal Charge Lewis Structure Craftukrain Vrogue Co Calculating formal charge from lewis structures assign formal charges to each atom in the interhalogen ion icl 4 −. icl 4 −. solution. step 1. we divide the bonding electron pairs equally for all i–cl bonds: step 2. we assign lone pairs of electrons to their atoms. each cl atom now has seven electrons assigned to it, and the i atom has. Formal charge is based on lewis structure. only covalent bonds have formal charges. formal charge calculation example. as an example, let's calculate the formal charges for carbon dioxide. remember, carbon dioxide has a central carbon double bonded to two oxygens. let's start with the formal charge of the oxygen atoms. oxygen is in group six.

Comments are closed.