Bragg S Law For X Ray Diffraction In Crystal Solid State Physics 1

X Ray Diffraction Definition Diagram Equation Facts Britannica Bragg’s law is a special case of laue diffraction, which determines the angles of coherent and incoherent scattering from a crystal lattice. when x rays are incident on a particular atom, they make an electronic cloud move like an electromagnetic wave. the movement of these charges radiates waves again with similar frequency, slightly blurred. Bragg's law. bragg's law is the result of experiments derived by physicist sir william lawrence bragg in 1912 and first presented on the same year to the cambridge philosophical society.\(^{[1]}\) william lawrence bragg and his father, sir william henry bragg, were awarded the nobel prize in physics in 1915 for their work in determining crystal structures beginning with nacl, zns, and diamond.

X Ray Diffraction Xrd Basics And Application Chemistry Libretexts Chapter 3 x ray diffraction. consider a crystal as made out of parallel planes of ions, spaced a distance d apart. the conditions for a sharp peak in the intensity of the scattered radiation are. bragg’s condition. bragg angle θ is just the half of the total angle 2 θ which the incident beam is deflected. Bragg diffraction (also referred to as the bragg formulation of x ray diffraction) was first proposed by lawrence bragg and his father, william henry bragg, in 1913 [1] after their discovery that crystalline solids produced surprising patterns of reflected x rays (in contrast to those produced with, for instance, a liquid). they found that these crystals, at certain specific wavelengths and. The result is bragg’s law of diffraction: mλ = 2d sin θ, m = 1, 2, 3 …. (bragg's law) (7.1.1) if only two rows are involved, the transition from constructive to destructive interference as θ changes is gradual. however, if interference from many rows occurs, then the constructive interference peaks become very sharp with mostly. Bragg spectrometer much of our knowledge about crystal structure and the structure of molecules as complex as dna in crystalline form comes from the use of x rays in x ray diffraction studies. a basic instrument for such study is the bragg spectrometer. to obtain nearly monochromatic x rays, an x ray tube is used to produce characteristic x rays.

Bragg S Law And Diffraction The result is bragg’s law of diffraction: mλ = 2d sin θ, m = 1, 2, 3 …. (bragg's law) (7.1.1) if only two rows are involved, the transition from constructive to destructive interference as θ changes is gradual. however, if interference from many rows occurs, then the constructive interference peaks become very sharp with mostly. Bragg spectrometer much of our knowledge about crystal structure and the structure of molecules as complex as dna in crystalline form comes from the use of x rays in x ray diffraction studies. a basic instrument for such study is the bragg spectrometer. to obtain nearly monochromatic x rays, an x ray tube is used to produce characteristic x rays. Now i am going to give you the top view of the diffractometer. it is essentially the combination of an x ray generator, a specimen holder and a detector. the top view has x ray coming in. this is monochromatic x ray, some lambda fixed, coming in. top view has this sitting in a carousel, and this carousel spins. and then i have a detector. The main idea. bragg's law is a phenomenon in physics that relates the angles for coherent & incoherent scattering of crystal lattices, the wavelength of the incident wave, and the distance that the wave travels; the distance traveled by the wave depends on the separation of the layers and the angle at which the x ray entered the material.
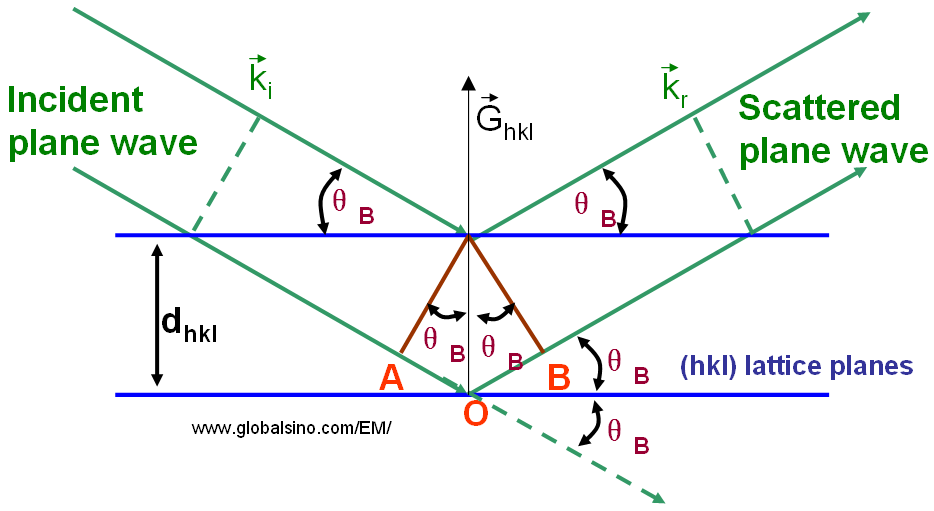
Bragg Condition Law Bragg Scattering Bragg Angle Now i am going to give you the top view of the diffractometer. it is essentially the combination of an x ray generator, a specimen holder and a detector. the top view has x ray coming in. this is monochromatic x ray, some lambda fixed, coming in. top view has this sitting in a carousel, and this carousel spins. and then i have a detector. The main idea. bragg's law is a phenomenon in physics that relates the angles for coherent & incoherent scattering of crystal lattices, the wavelength of the incident wave, and the distance that the wave travels; the distance traveled by the wave depends on the separation of the layers and the angle at which the x ray entered the material.

Bragg Law Definition Equation Diagram Facts Britannica

Comments are closed.