Bragg S Equation For X Ray Diffraction In Chemistry Practice

Bragg S Equation For X Ray Diffraction In Chemistry Practice Problems This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the use of bragg's equation for x ray diffraction. it explains how to use the equation to c. After wilhelm roentgen discovered x rays in 1895, william henry bragg pioneered the determination of crystal structure by x ray diffraction methods, began a lifelong investigation of the nature of radiation, principally x rays but also alpha and beta particles and gamma rays. after the discovery of the diffraction of x rays by crystals in 1912.

X Ray Diffraction Definition Diagram Equation Facts Britannica Practice problems exams and quizzes diffraction, and bragg's law – 3.091 introduction to solid state chemistry – fall 2018. x ray generation, diffraction. The relationship describing the angle at which a beam of x rays of a particular wavelength diffracts from a crystalline surface was discovered by sir william h. bragg and sir w. lawrence bragg and is known as bragg’s law. 2dsinθ = nλ. λ = wavelength of the x ray. θ = scattering angle. n = integer representing the order of the diffraction. Introduction. bragg’s law was introduced by sir w.h. bragg and his son sir w.l. bragg. the law states that when the x ray is incident onto a crystal surface, its angle of incidence, θ θ, will reflect back with a same angle of scattering, θ θ. and, when the path difference, d d is equal to a whole number, n n, of wavelength, a constructive. Donate here: aklectures donate website video link: aklectures lecture x ray diffraction and bragg equationfacebook link: htt.
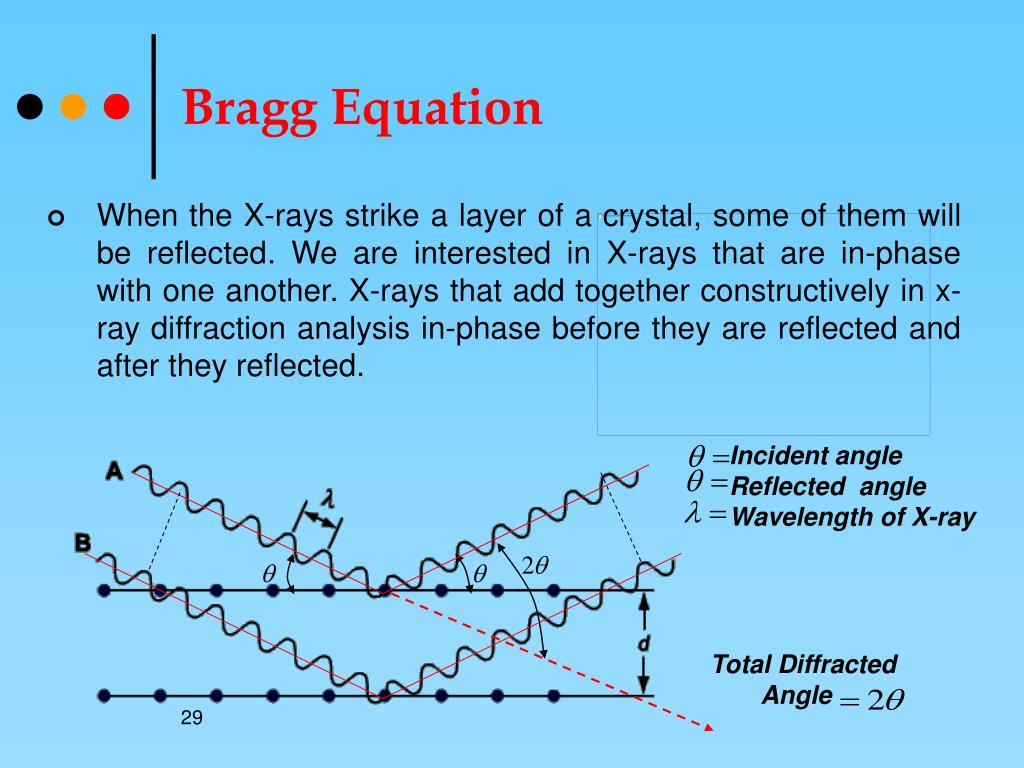
Ppt Chapter 3 X Ray Diffraction In Crystal Powerpoint Presentation Introduction. bragg’s law was introduced by sir w.h. bragg and his son sir w.l. bragg. the law states that when the x ray is incident onto a crystal surface, its angle of incidence, θ θ, will reflect back with a same angle of scattering, θ θ. and, when the path difference, d d is equal to a whole number, n n, of wavelength, a constructive. Donate here: aklectures donate website video link: aklectures lecture x ray diffraction and bragg equationfacebook link: htt. Typical derivations of the bragg equation in introductory texts do not adequately explain why x rays are reflected as if by a mirror by crystal planes, and often lead to the mistaken idea that lattice points can be identified with the centres of atoms or ions in the structure. the treatment offered here is a little more demanding, but to compensate for this also has the advantage that it can. The bragg condition gives the angle at which coherent scattering occurs as a function of the wavelength of the incident light and the periodicity of the lattice: nλ = 2d sin θ n λ = 2 d sin. . θ. this equation is the condition for constructive interference, and n n is an integer (n = 1 n = 1 dominates for most lattices), λ λ is the.

юааbraggтащsюаб Law Definition Derivation юааequationюаб Applications Examples Typical derivations of the bragg equation in introductory texts do not adequately explain why x rays are reflected as if by a mirror by crystal planes, and often lead to the mistaken idea that lattice points can be identified with the centres of atoms or ions in the structure. the treatment offered here is a little more demanding, but to compensate for this also has the advantage that it can. The bragg condition gives the angle at which coherent scattering occurs as a function of the wavelength of the incident light and the periodicity of the lattice: nλ = 2d sin θ n λ = 2 d sin. . θ. this equation is the condition for constructive interference, and n n is an integer (n = 1 n = 1 dominates for most lattices), λ λ is the.
Bragg S Law Of X Ray Diffraction Download Scientific Diagram

Comments are closed.