Basics Of Vector Analysis With Solved Examples

Solution Vector Analysis With Examples Studypool For the given example, the average velocity will be 500 35= 14.29 km min. there is also a difference between instantaneous velocity and average velocity, just as speed. the instantaneous velocity of the object for example would be 300 15= 20 km min in the north direction when the body is moving from point a to b. 6 chapter 1 vector analysis exercises 1.1.1 show how to find a and b,givena b and a −b. 1.1.2 the vector a whose magnitude is 1.732 units makes equal angles with the coordinate axes. find ax,ay, and az. 1.1.3 calculate the components of a unit vector that lies in the xy plane and makes equal angles with the positive directions of the x and.
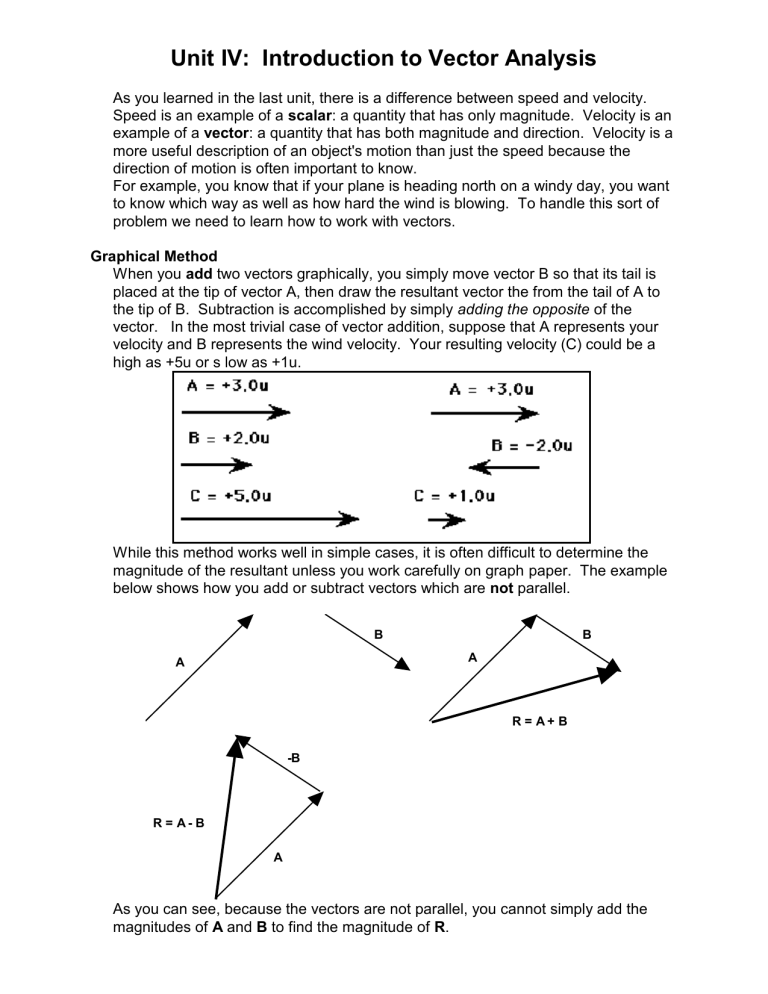
Vector Analysis The vectors at the tail of a and goes to the tip of b is defined to be. there is an equivalent construction for the law of vector. and b can be drawn with their tails at the same point. the two vectors form the g sides g g to the vector c = a of a parallelogram. the diagonal of the parallelogram corresponds. 1.2 vector algebra there are two basic operations with vectors: (a) vector addition; (b) scalar multiplication. (a) vector addition consider vectors a and b, pictured in fig. 1 2(a). the sum or resultant of a and b, is a vector c formed by placing theinitial pointofb onthe terminalpointofaand then joiningthe initial pointofato the terminal. Properties of vectors. a vector is a quantity that has both direction and magnitude. let a vector be denoted by the symbol a→ a →. the magnitude of a→ a → is |a→| ≡ a | a → | ≡ a. we can represent vectors as geometric objects using arrows. the length of the arrow corresponds to the magnitude of the vector. the arrow points in. Summary of properties of vector product. a × b = −b × a. a × b = 0 if a, b are parallel. a × (b c) = a × b a × c. a × (αb) = αa × b. ctor multiplication and geometrical applications3.1 the scalar triple productby introducing a third vector, we extend the geometrical idea of an area to th.

Comments are closed.