B Cell Activation And Class Switching Immunology Physiology Series

B Cell Activation And Class Switching Immunology Physiology Series B cell (b lymphocyte) activation and class switching | immunology | physiology lecture series (medicosis physiology playlist).🍱 endocrine pharmacology cours. In addition, the activation of b cells expressing igm containing bcrs is more sensitive to the change in mechanical forces in the initiation of bcr signaling than is the activation of b cells.
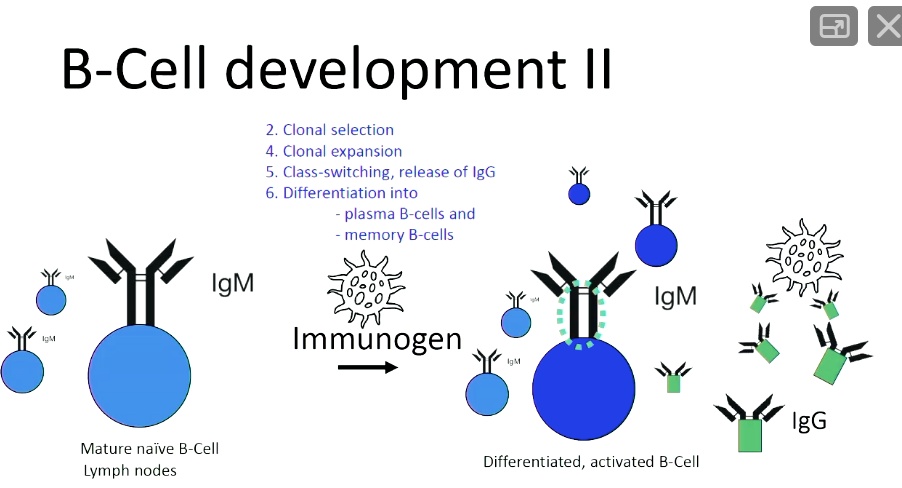
Solved B Cell Development Ii Clonal Selection Clonal Expansion Class switch recombination (csr) occurs between switch (s) regions located upstream of each of the c h regions except cδ and results in a change from igm and igd expression by naive b cells to expression of one of the downstream isotypes. igd expression occurs by alternative transcription termination splicing of the cμ cδ genes. The b1, mz, and gc b cell subsets all contribute to the circulating natural antibody pool, thymic independent igm antibody responses, and adaptive immunity by terminal differentiation into plasma cells, the effector cells of humoral immunity. 67 antigen activation of mature b cells leads initially to gc development, the transient generation of. Mechanism of class switch recombination that allows isotype switching in activated b cells. immunoglobulin class switching, also known as isotype switching, isotypic commutation or class switch recombination (csr), is a biological mechanism that changes a b cell's production of immunoglobulin from one type to another, such as from the isotype igm to the isotype igg. [1]. During immune responses, b cells generate functionally diverse secreted antibodies through cellular differentiation and class switch recombination. horton et al. reveal that distinct clonal mechanisms regulate alternative b cell fate decisions. for class switching, the intersection of two cell autonomous stochastic events is required. a mathematical model utilizing molecular information and.
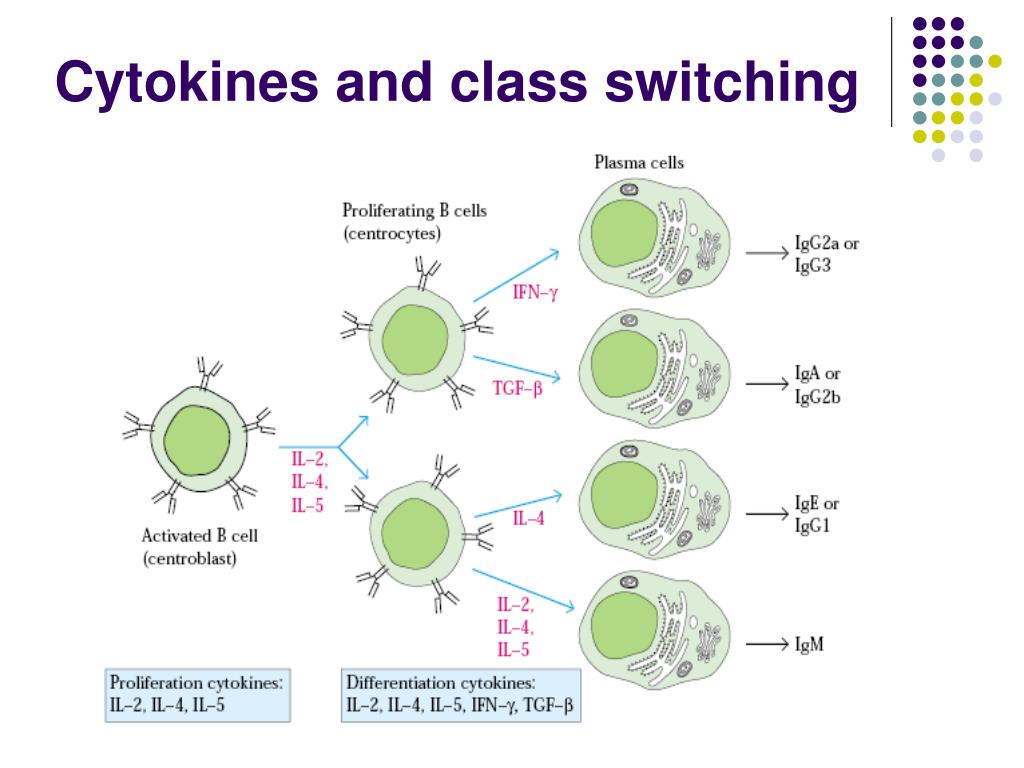
Ppt B Cell Response Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6833647 Mechanism of class switch recombination that allows isotype switching in activated b cells. immunoglobulin class switching, also known as isotype switching, isotypic commutation or class switch recombination (csr), is a biological mechanism that changes a b cell's production of immunoglobulin from one type to another, such as from the isotype igm to the isotype igg. [1]. During immune responses, b cells generate functionally diverse secreted antibodies through cellular differentiation and class switch recombination. horton et al. reveal that distinct clonal mechanisms regulate alternative b cell fate decisions. for class switching, the intersection of two cell autonomous stochastic events is required. a mathematical model utilizing molecular information and. Not only the cellular protein profile support b cell proliferation in the gc dark zone , but also some environmental factors, such as hypoxia, can increase the expression of activation induced cytidine deaminase (aid), thereby inhibiting the activity of mtorc1 induced differentiation of gc b cells, and promoting antibody class switch [69, 70. Upon b cell activation, the immunoglobulin locus undergoes a series of genetic modifications to alter the binding capacity and effector function of secreted antibodies. this process is highlighted by a genomic recombination event known as class switch recombination (csr) in which the default igm antibody isotype is substituted for one of igg.

The Adaptive Immune Response B Lymphocytes And Antibodies Anatomy Not only the cellular protein profile support b cell proliferation in the gc dark zone , but also some environmental factors, such as hypoxia, can increase the expression of activation induced cytidine deaminase (aid), thereby inhibiting the activity of mtorc1 induced differentiation of gc b cells, and promoting antibody class switch [69, 70. Upon b cell activation, the immunoglobulin locus undergoes a series of genetic modifications to alter the binding capacity and effector function of secreted antibodies. this process is highlighted by a genomic recombination event known as class switch recombination (csr) in which the default igm antibody isotype is substituted for one of igg.

B Cells British Society For Immunology

Comments are closed.