Atom Chemistry Dictionary Glossary
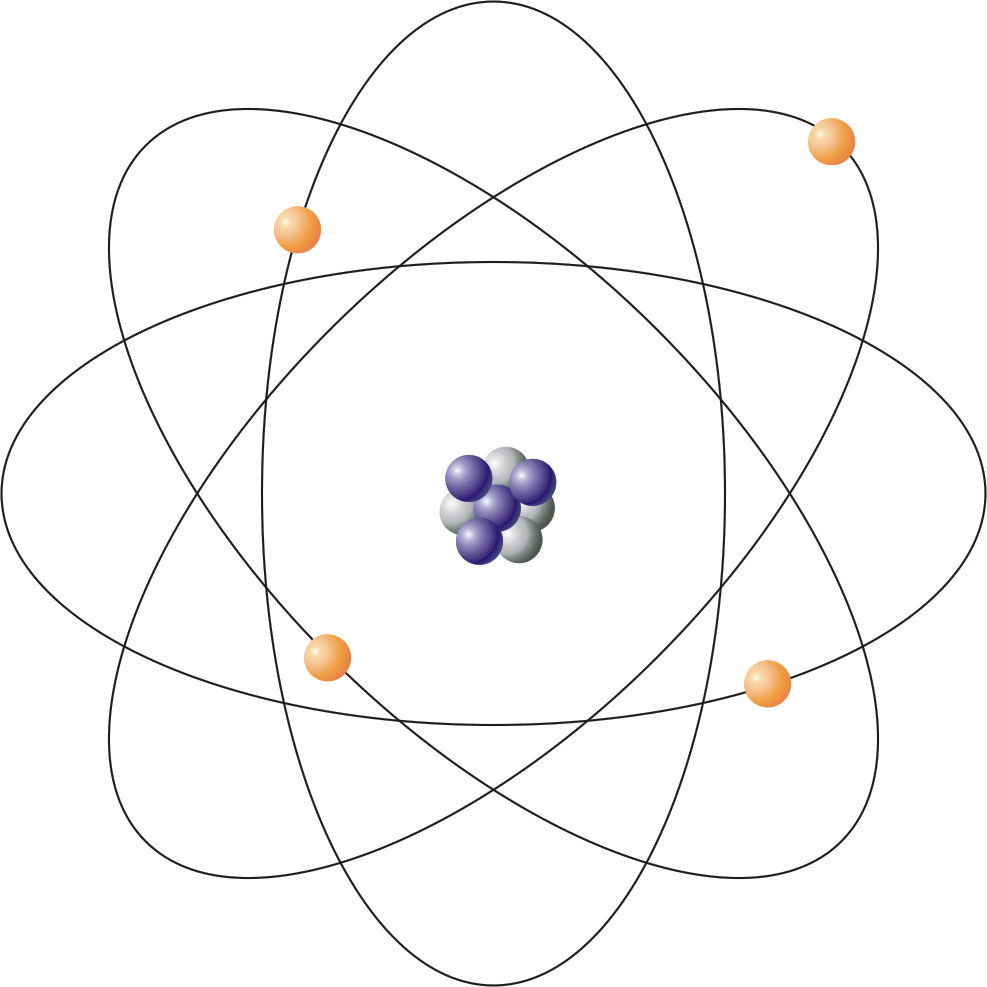
Atom Chemistry Dictionary Glossary Where x is the parent atom, y is the daughter atom, z is the atomic mass of x, a is the atomic number of x. example: 238 u 92 decays by alpha decay into 234 th 90. alpha hydrogen – an alpha hydrogen is a hydrogen atom bonded to the α carbon in a molecule. α hydrogen is the most common notation for alpha hydrogen. Atom is an atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of the element. rutherford bohr’s model represents the atom as a positively charged core of a size around 10 14 m composed of protons (positive particles) and neutrons (neutral particles) around which negatively charged electrons circle.

Periodic Table Of The Elements Chemistry Dictionary Glossary Search results for 'atom'. the chemistry glossary contains basic information about basic terms in chemistry, physical quantities, measuring units, classes of compounds and materials and important theories and laws. This glossary of chemistry terms is a list of terms and definitions relevant to chemistry, including chemical laws, diagrams and formulae, laboratory tools, glassware, and equipment. chemistry is a physical science concerned with the composition, structure, and properties of matter , as well as the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions. A to z chemistry dictionary. chemistry is full of precise definitions!. colin cuthbert science photo library getty images. this alphabetical chemistry dictionary offers definitions and examples of important chemistry and chemical engineering terms. for each term, a brief definition is given, and each link leads to a more comprehensive. Atom, the basic building block of all matter and chemistry. atoms can combine with other atoms to form molecules but cannot be divided into smaller parts by ordinary chemical processes. most of the atom is empty space. the rest consists of three basic types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/periodic-table-of-the-elements-and-molecules-582649268-594d736c3df78cae81f68ed4.jpg)
A To Z Chemistry Dictionary A to z chemistry dictionary. chemistry is full of precise definitions!. colin cuthbert science photo library getty images. this alphabetical chemistry dictionary offers definitions and examples of important chemistry and chemical engineering terms. for each term, a brief definition is given, and each link leads to a more comprehensive. Atom, the basic building block of all matter and chemistry. atoms can combine with other atoms to form molecules but cannot be divided into smaller parts by ordinary chemical processes. most of the atom is empty space. the rest consists of three basic types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. This means that nitrogen has 7 proton and 7 electron. mass number. it is total number of proton and neutron present in the nucleus of each atom of an element. mass number = no. of proton no of neutrons. = atomic number – no of neutron. for example: the mass number of fluorine is 19 and atomic number is 9. Atom definition. an atom is the basic building block of matter, consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons. an atom is the smallest unit of matter that forms a chemical element and cannot be divided using any chemical means. every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma consists of neutral or ionized atoms.

Comments are closed.