According To Standard Economic Theory Consumer Surplus Must Always Be

Explaining Consumer Surplus Economics Tutor2u According to standard economic theory, consumer surplus must always be at least zero we often simplify economic models by ignoring the role that transaction costs play in our decision making purchasing a good often involves explicit transaction costs, such as the cost of the gasoline used to get to the store but there are also implicit. According to standard economic theory consumer surplus must always be ebook subscription services according to standard economic theory consumer surplus must always be budget friendly options 6. navigating according to standard economic theory consumer surplus must always be ebook formats epub, pdf, mobi, and more.
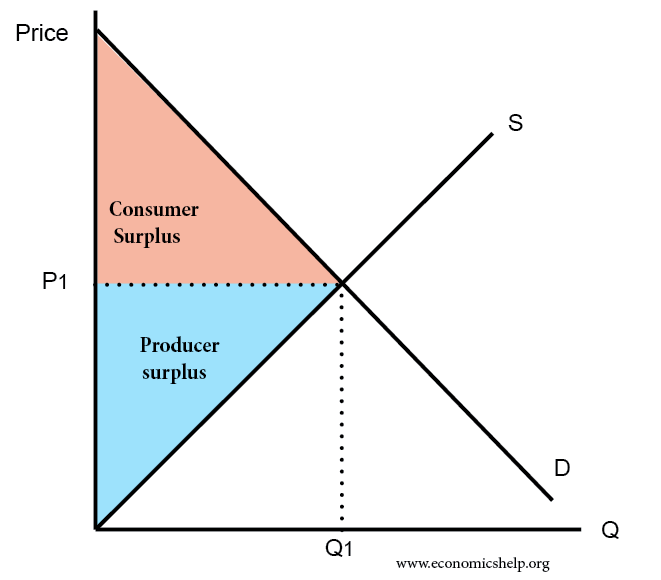
Definition Of Consumer Surplus Economics Help Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like willingness to pay estimates for environmental improvements a) should, in theory, be close estimates of the consumer surplus gained from public goods provided free of charge. b) should, according to standard economic theory, be much lower than willingness to accept estimates of consumer surplus. c) are generally much higher than. Obviously, you would never buy something if its valuation to you as a consumer was less than the price you must pay. therefore, according to standard economic theory, consumer surplus must always be at least zero—though it is typically positive for an individual consumer since it is unlikely that you actually pay the true valuation for any. Question: 2. the effect of transaction costs on decision making aa aa this wendy's commercial confuses the notions of appreciation and consumer surplus. recall that consumer surplus is the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and what he or she actually pays for it according to standard economic theory, consumer. Recall that consumer surplus is the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and what he or she actually pays for it. according to standard economic theory, consumer surplus must always economists often simplify economic models by ignoring the role that transaction costs play in decision making.

Explaining Consumer Surplus Tutor2u Economics Question: 2. the effect of transaction costs on decision making aa aa this wendy's commercial confuses the notions of appreciation and consumer surplus. recall that consumer surplus is the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and what he or she actually pays for it according to standard economic theory, consumer. Recall that consumer surplus is the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and what he or she actually pays for it. according to standard economic theory, consumer surplus must always economists often simplify economic models by ignoring the role that transaction costs play in decision making. Consumer surplus, also known as buyer’s surplus, is the economic measure of a customer’s excess benefit. it is calculated by analyzing the difference between the consumer’s willingness to pay for a product and the actual price they pay, also known as the equilibrium price. a surplus occurs when the consumer’s willingness to pay for a. According to standard economic theory consumer surplus must always be: the economic theory of the consumer e. antony selvanathan,1987 consumers' surplus and its usefulness as a decision criterion patrick c. mcmahon,ulrich schlieper,1971 consumption takes time ian steedman,2001 05 standard.

Comments are closed.