A Level Statistics 1 Chapter 6 Discrete Random Variables
Discrete Random Variable Variance Formula International alevel mathematics statistics 1 chapter 6 discrete random variables walkthrough. following the pearsons student book. these lessons have been r. Pearson edexcel ial statistics 1 unit 6 discrete random variables.

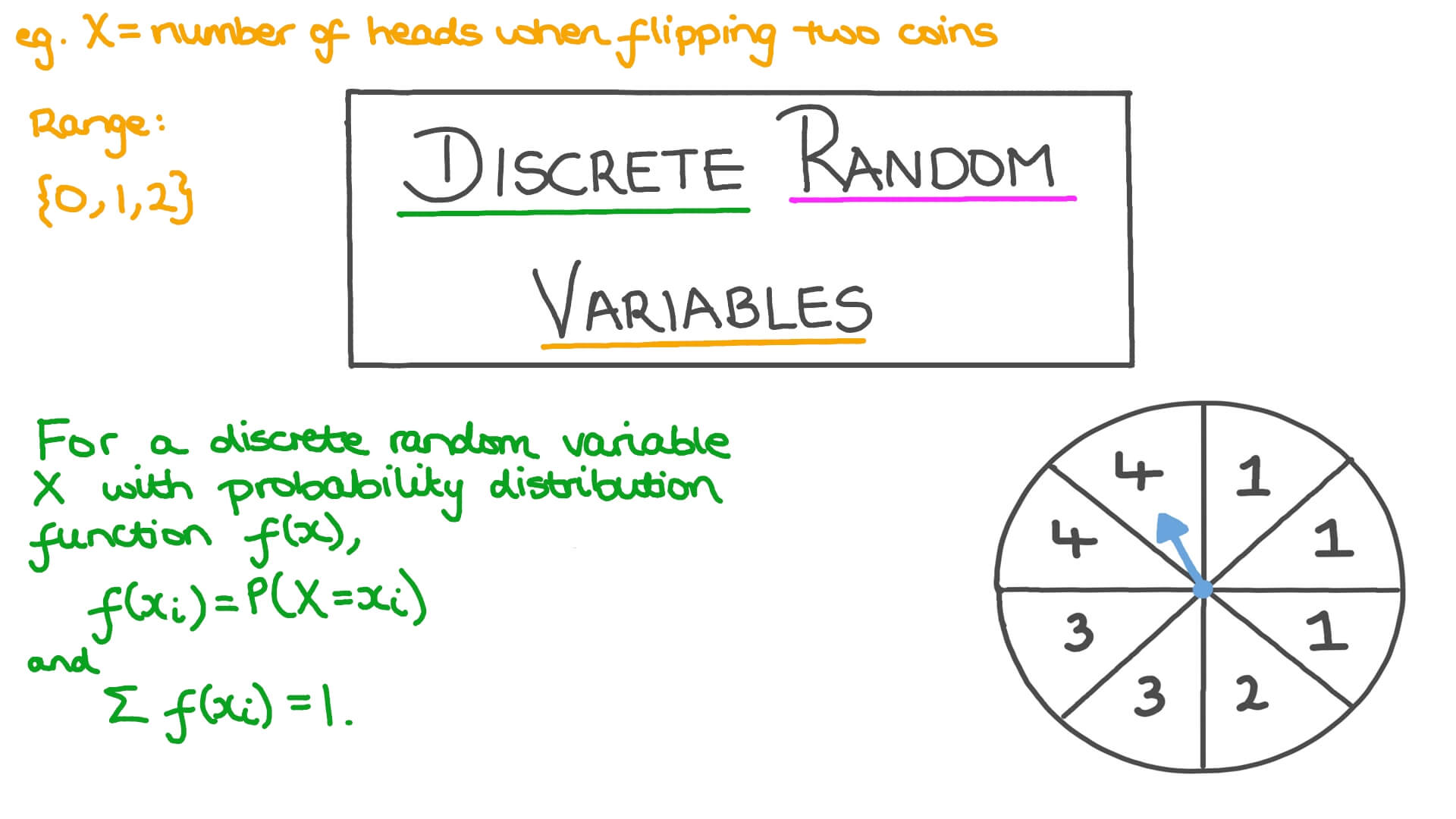
Chapter 6 Video 1 Discrete Random Variables Youtube 𝑘𝑘= 2,4, 6 = 8 𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜ℎ𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒. where k is a constant. a. show that k = 1 18 (2) b. find the exact value of f(5) (2) 2. the discrete random variable x can take only the values 1, 2 and 3. for these values the cumulative distribution function is define by, f(x) = 𝑥𝑥 3 𝑘𝑘 40 x. Example 1: a discrete random variable 𝑋𝑋 has the following probability distribution. a) find 𝑬𝑬(𝑿𝑿). b) find 𝑬𝑬(𝑿𝑿𝟐𝟐). some questions will also require you to use the fact that the sum of the probabilities for a discrete random variable must equate to 1: b) example 2: the random variable 𝑌𝑌 has the. The experiment consists of n identical trials as described in condition 1. the probability of success on any one trial is denoted by p and does not change from trial to trial. (note that the probability of a failure is (1−p) and also does not change from trial to trial.) the trials are independent. the binomial random variable is the count of. The probability of an outcome is between 0 and 1. the sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes is 1. the outcomes are mutually exclusive. a bimodal experiment consist of tossing 10 coins in observing the number of "heads" that land face up. identify any questions from the list that would usually be answered by using a cumulative.

25 Discrete Variable Examples 2024 The experiment consists of n identical trials as described in condition 1. the probability of success on any one trial is denoted by p and does not change from trial to trial. (note that the probability of a failure is (1−p) and also does not change from trial to trial.) the trials are independent. the binomial random variable is the count of. The probability of an outcome is between 0 and 1. the sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes is 1. the outcomes are mutually exclusive. a bimodal experiment consist of tossing 10 coins in observing the number of "heads" that land face up. identify any questions from the list that would usually be answered by using a cumulative. In general, p(x = x) = (5 6) (x 1) × (1 6) cumulative distribution function the cumulative distribution function (c.d.f.) of a discrete random variable x is the function f(t) which tells you the probability that x is less than or equal to t. Discrete random variable are random variable that can take on distinct and separate variable. a random variable is a function defined on the sample space. however, a discrete random variables is a variable that can only take a finite or countable number of values, and have a positive probability of taking each one. if x is a discrete random.

Comments are closed.