3 Muscles Crossing The Elbow Joint

3 Muscles Crossing The Elbow Joint Youtube Learn about the anatomy and structure of the elbow muscles with innerbody's interactive 3d model. the elbow is a synovial hinge joint located between the upper arm and forearm. it is formed by the meeting of three bones: the humerus in the upper arm and the ulna and radius in the lower arm. like all other hinge joints, the elbow permits. The elbow is an "intricate mechanical system." [1] it has three bones the humerus, radius and ulna and it is one of the most stable joints. [2] daily activities rely heavily on this stability. [3] therefore, any instability caused by injury to the elbow structures can cause pain and significantly impact daily and athletic performance.
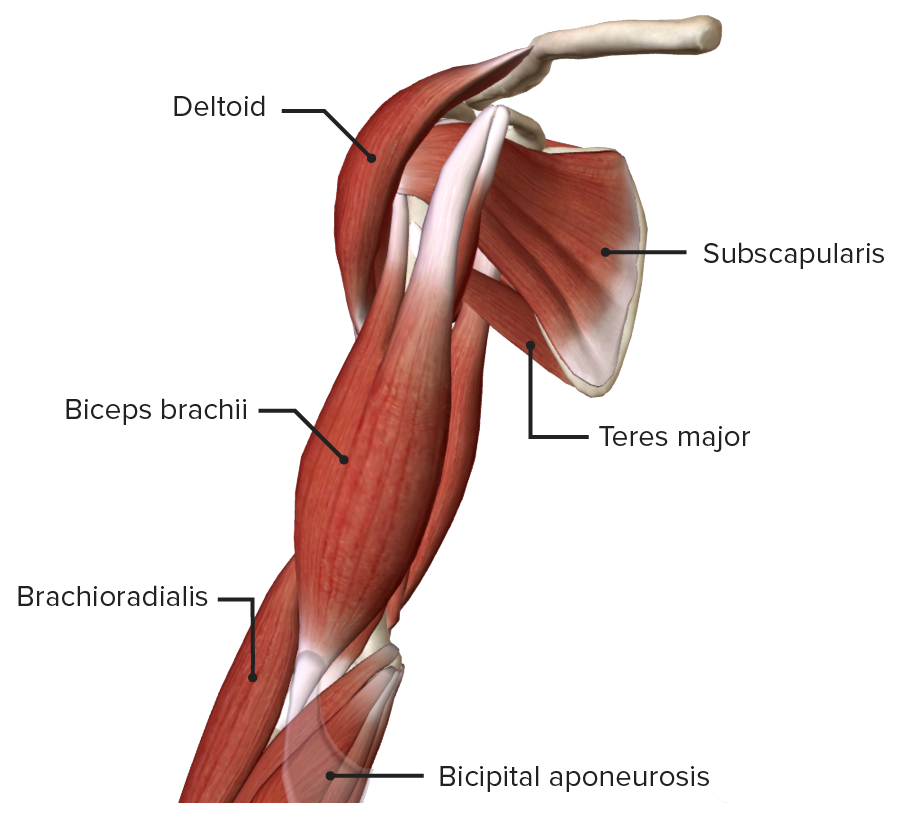
Elbow Joint Anatomy Video Lecturio Medical A: flexes the forearm. triceps brachii. a: extends the forearm. triceps brachii. o: below glenoid fossa (long head); posterior lateral humerus (lateral head); posterior humerus (medial head) triceps brachii. i: olecranon of ulna. anconeus. a: extends the forearm. 1 5. synonyms: none. the elbow joint is a synovial joint found in the upper limb between the arm and the forearm. it is the point of articulation of three bones: the humerus of the arm and the radius and the ulna of the forearm. the elbow joint is classified structurally as a synovial joint. it is also classified structurally as a compound. Medial lateral cords of the brachial plexus. anatomy at elbow. it courses with brachial artery, running from lateral to medial. lies superficial to brachialis muscle at level of elbow joint. innervation at elbow. it gives branches to elbow joint. it has no branches in upper arm. ulnar nerve. origin. The elbow joint is where your humerus (your upper arm bone) meets your radius and ulna (the two bones in your forearm). it joins your upper arm to your forearm. your elbow also contains cartilage, ligaments, muscles, nerves and blood vessels. your elbow moves in two main directions.

Muscles Crossing The Elbow Joint Diagram Quizlet Medial lateral cords of the brachial plexus. anatomy at elbow. it courses with brachial artery, running from lateral to medial. lies superficial to brachialis muscle at level of elbow joint. innervation at elbow. it gives branches to elbow joint. it has no branches in upper arm. ulnar nerve. origin. The elbow joint is where your humerus (your upper arm bone) meets your radius and ulna (the two bones in your forearm). it joins your upper arm to your forearm. your elbow also contains cartilage, ligaments, muscles, nerves and blood vessels. your elbow moves in two main directions. The majority of the muscles crossing the elbow serve to rotate the forearm or flex and extend the wrist or fingers. only a few muscles act primarily to move the elbow joint. by virtue of their joint reaction forces, all muscles that cross the elbow have the potential to provide increased joint stability by compressing the articular surfaces. Movements. the orientation of the bones forming the elbow joint produces a hinge type synovial joint, which allows for extension and flexion of the forearm: extension – triceps brachii and anconeus. flexion – brachialis, biceps brachii, brachioradialis. note – pronation and supination do not occur at the elbow – they are produced at the.
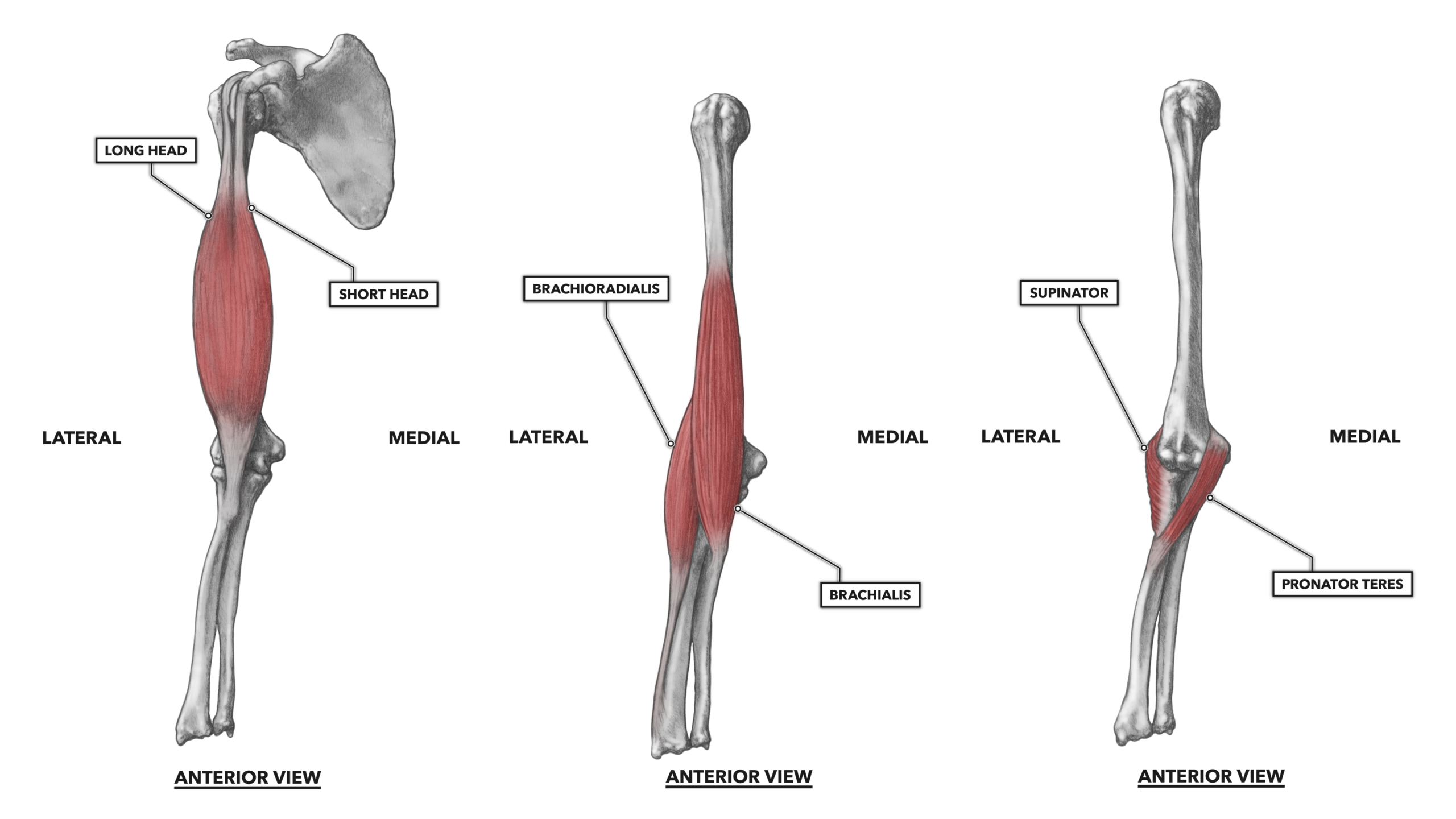
Elbow Muscles Diagram The majority of the muscles crossing the elbow serve to rotate the forearm or flex and extend the wrist or fingers. only a few muscles act primarily to move the elbow joint. by virtue of their joint reaction forces, all muscles that cross the elbow have the potential to provide increased joint stability by compressing the articular surfaces. Movements. the orientation of the bones forming the elbow joint produces a hinge type synovial joint, which allows for extension and flexion of the forearm: extension – triceps brachii and anconeus. flexion – brachialis, biceps brachii, brachioradialis. note – pronation and supination do not occur at the elbow – they are produced at the.

Muscles Crossing The Elbow Joint Flashcards Quizlet

Comments are closed.